Abstract
Summary
Patients with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) have an increased risk of osteoporosis related to inflammation. We evaluate the performance of low bone mineral density (BMD) in diagnosis of axSpA for patients with symptoms suggestive of the disease. A low BMD (T ≤ −2) could be an additional tool for the diagnosis of axSpA.
Introduction
Diagnosis of axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) can be challenging, especially in the absence of radiographic abnormalities. Patients with axSpA have an increased risk of osteoporosis related to inflammation. This study evaluated the performance of low bone mineral density (BMD) in diagnosis of axSpA for patients with symptoms suggestive of the disease.
Methods
Medical files of patients that visited a tertiary centre for symptoms suggestive of axSpA were reviewed. Two hundred and sixty-seven patients were classified in confirmed axSpA or unconfirmed axSpA according to the diagnosis of a senior rheumatologist. BMD measurements results and percentage of patients with a low BMD (T ≤ −2) at either spine or hip were compared between the two groups. Diagnostic performances of low BMD (specificity, sensitivity, positive, negative predictive values and positive likelihood ratio (LR+)) were assessed.
Results
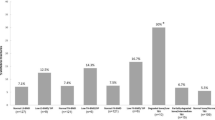
Compared to patients with unconfirmed axSpA (n = 74), patients with confirmed axSpA (n = 193) had similar age, were more frequently male, with positive HLA B27, higher disease duration and higher C-reactive protein (CRP). Low BMD was more frequent at spine and hip, in patients with confirmed (40.3 %) than unconfirmed axSpA (24.6 %, p = 0.021). The LR+ of low BMD for an axSpA diagnosis was 2.60 and 3.12 at the spine and hip. In the subgroup of patients without any radiographic abnormalities (n = 128), the LR+ of low BMD for an axSpA diagnosis was 2.90 and 2.54 at the spine and hip.
Conclusion
In patients with symptoms suggestive of axSpA, a low BMD (T ≤ −2) could be an additional tool for the diagnosis of axSpA.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Van der Linden S, Valkenburg HA, Cats A (1984) Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. A proposal for modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis Rheum 27:361–8
Amor B, Dougados M, Mijiyawa M (1990) Criteria of the classification of spondylarthropathies. Rev Rhum Mal Ostéo-Articul 57:85–9
Dougados M, van der Linden S, Juhlin R et al (1991) The European spondylarthropathy study group preliminary criteria for the classification of spondylarthropathy. Arthritis Rheum 199134:1218–27
Rudwaleit M, van der Heijde D, Landewé R et al (2009) The development of assessment of spondyloarthritis international society classification criteria for axial spondyloarthritis (part II): validation and final selection. Ann Rheum Dis 68:777–83
Feldtkeller E, Khan MA, van der Heijde D, van der Linden S, Braun J (2003) Age at disease onset and diagnosis delay in HLA-B27 negative vs. positive patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatol Int 23:61–6
Wallis D, Haroon N, Ayearst R, Carty A, Inman RD (2013) Ankylosing spondylitis and nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis: part of a common spectrum or distinct diseases? J Rheumatol 40:2038–41
Rudwaleit M, Haibel H, Baraliakos X et al (2009) The early disease stage in axial spondylarthritis: results from the German spondyloarthritis inception cohort. Arthritis Rheum 60:717–27
Kiltz U, Baraliakos X, Karakostas P et al (2012) Do patients with non-radiographic axial spondylarthritis differ from patients with ankylosing spondylitis? Arthritis Care Res 64:1415–22
Calin A (1991) Osteoporosis and ankylosing spondylitis. Br J Rheumatol 30:318–9
Baek HJ, Kang SW, Lee YJ et al (2005) Osteopenia in men with mild and severe ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatol Int 26:30–4
El Maghraoui A, Borderie D, Cherruau B, Edouard R, Dougados M, Roux C (1999) Osteoporosis, body composition, and bone turnover in ankylosing spondylitis. J Rheumatol 126:2205–9
Roux C (2011) Osteoporosis in inflammatory joint diseases. Osteoporos Int 22:421–33
Cooper C, Carbone L, Michet CJ, Atkinson EJ, O’Fallon WM, Melton LJ 3rd (1994) Fracture risk in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a population based study. J Rheumatol 1877–82
Will R, Palmer R, Bhalla AK, Ring F, Calin A (1989) Osteoporosis in early ankylosing spondylitis: a primary pathological event? Lancet 12:1483–5
Toussirot E, Michel F, Wendling D (2001) Bone density, ultrasound measurements and body composition in early ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatol Oxf Engl 40:882–8
Klingberg E, Lorentzon M, Mellström D et al (2012) Osteoporosis in ankylosing spondylitis—prevalence, risk factors and methods of assessment. Arthritis Res Ther 14:R108
Briot K, Durnez A, Paternotte S, Miceli-Richard C, Dougados M, Roux C (2013) Bone oedema on MRI is highly associated with low bone mineral density in patients with early inflammatory back pain: results from the DESIR cohort. Ann Rheum Dis 72:1914–9
Karberg K, Zochling J, Sieper J, Felsenberg D, Braun J (2005) Bone loss is detected more frequently in patients with ankylosing spondylitis with syndesmophytes. J Rheumatol 32:1290–8
Szulc P, Garnero P, Claustrat B, Marchand F, Duboeuf F, Delmas PD (2002) Increased bone resorption in moderate smokers with low body weight: the Minos study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87:666–74
Gratacós J, Collado A, Pons F et al (1999) Significant loss of bone mass in patients with early, active ankylosing spondylitis: a followup study. Arthritis Rheum 42:2319–24
Akgöl G, Kamanli A, Ozgocmen S (2014) Evidence for inflammation-induced bone loss in non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis. Rheumatolojy (Oxford) 53:497–501
Im CH, Kang EH, Ki JY et al (2009) Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand-mediated osteoclastogenesis is elevated in ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 27:620–5
Taylan A, Sari I, Akinci B et al (2012) Biomarkers and cytokines of bone turnover: extensive evaluation in a cohort of patients with ankylosing spondylitis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 13:191
Rauner M, Stupphann D, Haas M et al (2009) The HLA-B27 transgenic rat, a model of spondyloarthritis, has decreased bone mineral density and increased RANKL to osteoprotegerin mRNA ratio. J Rheumatol 36:120–6
Moltó A, Paternotte S, Comet DT et al (2013) Performances of the assessment of spondyloarthritis international society axial spondyloarthritis criteria for diagnostic and classification purposes in patients visiting a rheumatologist because of chronic back pain: results from a multicenter, cross-sectional study. Arthritis Care Res 65:1472–81
McGee S (2002) Simplifying likelihood ratios. J Gen Intern Med 17:646–9
Moltó A, Paternotte S, van der Heijde D, Claudepierre P, Rudwaleit M, Dougados M (2014) Evaluation of the validity of the different arms of the ASAS set of criteria for axial spondyloarthritis and description of the different imaging abnormalities suggestive of spondyloarthritis: data from the DESIR cohort. Ann Rheum Dis. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204262
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Forien, M., Moltó, A., Etcheto, A. et al. Bone mineral density in patients with symptoms suggestive of spondyloarthritis. Osteoporos Int 26, 1647–1653 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-015-3044-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-015-3044-y