Abstract
Objective
To report on intra-observer, inter-observer, and inter-method reliability and agreement for radiological measurements used in the diagnosis of hip dysplasia at skeletal maturity, as obtained by a manual and a digital measurement technique.
Materials and methods
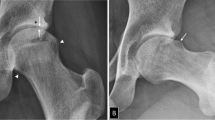
Pelvic radiographs from 95 participants (56 females) in a follow-up hip study of 18- to 19-year-old patients were included. Eleven radiological measurements relevant for hip dysplasia (Sharp’s, Wiberg’s, and Ogata’s angles; acetabular roof angle of Tönnis; articulo-trochanteric distance; acetabular depth-width ratio; femoral head extrusion index; maximum teardrop width; and the joint space width in three different locations) were validated. Three observers measured the radiographs using both a digital measurement program and manually in AgfaWeb1000. Inter-method and inter- and intra-observer agreement were analyzed using the mean differences between the readings/readers, establishing the 95% limits of agreement. We also calculated the minimum detectable change and the intra-class correlation coefficient.
Results
Large variations among different radiological measurements were demonstrated. However, the variation was not related to the use of either the manual or digital measurement technique. For measurements with greater absolute values (Sharp’s angle, femoral head extrusion index, and acetabular depth-width ratio) the inter- and intra-observer and inter-method agreements were better as compared to measurements with lower absolute values (acetabular roof angle, teardrop and joint space width).
Conclusion
The inter- and intra-observer variation differs notably across different radiological measurements relevant for hip dysplasia at skeletal maturity, a fact that should be taken into account in clinical practice. The agreement between the manual and digital methods is good.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Engesæter IØ, Lehmann T, Laborie LB, Lie SA, Rosendahl K, Engesæter LB. Total hip replacement in young adults with hip dysplasia: age at diagnosis, previous treatment, quality of life, and validation of diagnoses reported to the Norwegian Arthroplasty Register between 1987 and 2007. Acta Orthop. 2011;82(2):149–154.
Dezateux C, Rosendahl K. Developmental dysplasia of the hip. Lancet. 2007;369(9572):1541–52.
Eastwood DM. Neonatal hip screening. Lancet. 2003;361(9357):595–7.
Wiberg G. Studies on dysplastic acetabula and congenital subluxation of the hip joint. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl. 1939;58:1–132.
Sharp IK. Acetabular dysplasia. J Bone Jt Surg. 1961;43B(2):268–72.
Cooperman DR, Wallensten R, Stulberg SD. Acetabular dysplasia in the adult. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983;175:79–85.
Stulberg SD, Harris WH. Acetabular dysplasia and development of osteoarthritis of the hip. In: Harris WH, editor. The hip proceedings of the Second Open Scientific Meeting of the Hip Society. St Louis: Mosby; 1974. p. 82–93.
Heyman CH, Herndon CH. Legg-Perthes disease; a method for the measurement of the roentgenographic result. J Bone Jt Surg Am. 1950;32(A:4):767–78.
Nelitz M, Guenther KP, Gunkel S, Puhl W. Reliability of radiological measurements in the assessment of hip dysplasia in adults. Br J Radiol. 1999;72(856):331–4.
Mast NH, Impellizzeri F, Keller S, Leunig M. Reliability and agreement of measures used in radiographic evaluation of the adult hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469(1):188–99.
Troelsen A, Romer L, Kring S, Elmengaard B, Soballe K. Assessment of hip dysplasia and osteoarthritis: variability of different methods. Acta Radiol. 2010;51(2):187–93.
Pedersen DR, Lamb CA, Dolan LA, Ralston HM, Weinstein SL, Morcuende JA. Radiographic measurements in developmental dysplasia of the hip: reliability and validity of a digitizing program. J Pediatr Orthop. 2004;24(2):156–60.
Tönnis D. Normal values of the hip joint for the evaluation of X-rays in children and adults. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976;119:39–47.
Tönnis D, Brunken D. Differentiation of normal and pathological acetabular roof angle in the diagnosis of hip dysplasia. Evaluation of 2294 acetabular roof angles of hip joints in children. Arch Orthop Unfallchir. 1968;64(3):197–228.
Tönnis D, Legal H, Graf R. Congenital dysplasia and dislocation of the hip in children and adults. New York: Springer-Verlag; 1987.
Ogata S, Moriya H, Tsuchiya K, Akita T, Kamegaya M, Someya M. Acetabular cover in congenital dislocation of the hip. J Bone Jt Surg Br. 1990;72(2):190–6.
Albinana J, Morcuende JA, Weinstein SL. The teardrop in congenital dislocation of the hip diagnosed late. A quantitative study. J Bone Jt Surg Am. 1996;78(7):1048–55.
Langenskiold A, Salenius P. Epiphyseodesis of the greater trochanter. Acta Orthop Scand. 1967;38(2):199–219.
Jacobsen S, Sonne-Holm S, Soballe K, Gebuhr P, Lund B. Joint space width in dysplasia of the hip: a case-control study of 81 adults followed for ten years. J Bone Jt Surg Br. 2005;87(4):471–7.
Bland JM, Altman DG. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet. 1986;1(8476):307–10.
Bland JM, Altman DG. Measuring agreement in method comparison studies. Stat Methods Med Res. 1999;8(2):135–60.
Bland JM, Altman DG. Agreement between methods of measurement with multiple observations per individual. J Biopharm Stat. 2007;17(4):571–82.
McGraw KO, Wong SP. Forming inferences about some intraclass correlation coefficients. Psychol Methods. 1996;1(1):30–46.
de Vet HC, Terwee CB, Knol DL, Bouter LM. When to use agreement versus reliability measures. J Clin Epidemiol. 2006;59(10):1033–9.
Petrie A. Statistics in orthopaedic papers. J Bone Jt Surg Br. 2006;88(9):1121–36.
Bland JM, Altman DG. A note on the use of the intraclass correlation coefficient in the evaluation of agreement between two methods of measurement. Comput Biol Med. 1990;20(5):337–40.
Altman DG. Practical statistics for medical research. London: Chapman & Hall; 1991.
Lequesne M, Malghem J, Dion E. The normal hip joint space: variations in width, shape, and architecture on 223 pelvic radiographs. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004;63(9):1145–51.
Tannast M, Mistry S, Steppacher SD, Reichenbach S, Langlotz F, Siebenrock KA, et al. Radiographic analysis of femoroacetabular impingement with Hip2Norm—reliable and validated. J Orthop Res. 2008;26(9):1199–205.
Delaunay S, Dussault RG, Kaplan PA, Alford BA. Radiographic measurements of dysplastic adult hips. Skelet Radiol. 1997;26(2):75–81.
Acknowledgments
We thank radiographer Sigrun Tufta for performing all the high quality radiographs and dr Martin Biermann for all help and advice in the process of converting the pelvic radiographs to DICOM files. The study has received funding from University of Bergen and Arthritis Research UK (grant Ref 18196). Two of the authors (I.Ø.E., L.B.L.) are supported financially by Western Norway Regional Health Authority and one author (T.G.L.) by the Frank Mohn Foundation.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Engesæter, I.Ø., Laborie, L.B., Lehmann, T.G. et al. Radiological findings for hip dysplasia at skeletal maturity. Validation of digital and manual measurement techniques. Skeletal Radiol 41, 775–785 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-011-1283-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-011-1283-3