Abstract
Background
Selective steroid injections of the lumbar spine carry a risk of paraplegia of sudden onset. Seven cases have been reported in the English literature since 2002.
Materials and methods
Five new cases have been analyzed, all coming from Paris area centers. Injections were performed between 2003 and 2008. The following items were searched for: location of a previous lumbar spine surgery if any, symptoms indicating the procedure, route of injection, imaging technique used for needle guidance, injection of a contrast medium, type of steroid, other drugs injected if any, paraplegia level, post-procedure MR findings. The current and reported cases were compared.
Results
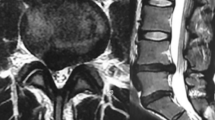
MR findings were consistent with spinal cord ischemia of arterial origin. The high rate of patients who had been operated on in these cases does not correspond to that of patients undergoing injections. The presence of epidural scar might increase the risk. The foraminal route was the only one involved in nonoperated patients. Foraminal, interlaminar, or juxta-zygoapophyseal routes were used in operated-on patients.
Conclusion
The high rate of French cases when compared to the literature might arise from the almost exclusive use of prednisolone acetate, a molecule with a high tendency to coalesce in macro-aggregates, putting the spinal cord at risk of arterial supply embolization.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Houten JK, Errico TJ (2002) Paraplegia after lumbosacral nerve root block: report of three cases. Spine J 2:70–75
Huntoon MA, Martin DP (2004) Paralysis after transforaminal epidural injection and previous spinal surgery. Reg Anesth Pain Med 29:494–495
Somayaji HS, Saifuddin A, Casey ATH, Briggs TWR (2005) Spinal cord infarction following therapeutic computed tomography-guided left L2 nerve root injection. Spine 30:E106–E108
Quintero N, Laffont I, Bouhmidi L, Rech C, Even Schneider A, Gavardin T, Dizien O (2006) Transforaminal epidural steroid injection and paraplegia: case report and bibliographic review. Ann Readapt Med Phys 49:242–247
Glaser SE, Falco F (2005) Paraplegia following a thoracolumbar transforaminal epidural steroid injection. Pain Physician 8:309–314
Lenoir T, Deloin X, Dauzac C, Rillardon L, Guigui P (2008) Paraplegia after interlaminar epidural steroid injection: a case report. Rev Chir Orthop 94:697–701
Tajima T, Furukawa K, Kuramochi E (1980) Selective lumbosacral radiculography and block. Spine 5:68–77
Martin DP, Huntoon MA (2005) Spinal cord infarction following therapeutic computed tomography-guided left L2 nerve root injection. Spine 30:1558
Yuh WT, Marsh EE, Wang AK, Russell JW, Koci TM, Ryals TJ (1992) MR imaging of spinal cord and vertebral body infarction. Am J Neuroradiol 13:145–154
Thron AK (1988) Vascular anatomy of the spinal cord. Neuroradiological investigations and clinical syndromes. Springer-Verlag, Wien, pp 8–12
Mawad M, Rivera V, Crawford S, Ramirez A, Breitbach W (1990) Spinal cord ischemia after resection of thoracoabdominal aneurysms: MR findings in 24 patients. AJNR 11:987–991
Mc Lain RF, Fry M, Hecht ST (1997) Transient paralysis associated with epidural steroid injection. J Spinal Disord 10:441–444
Osborn AG (1994) Diagnostic neuroradiology. Mosby, St. Louis
Toro G, Roman GC, Navarro-Roman L, Cantillo J, Serrano B, Vergara I (1994) Natural history of spinal cord infarction caused by nucleus pulposus embolism. Spine 19:360–366
Djindjian R, Hurth M, Houdart R (1970) Angiography of the spinal cord. Masson, Paris, pp 1–26
Bert S, Iyriboz AT, Barret F, Zouaoui A, Chiras J (1995) An angiographic study of the spinal vascularization at the thoracic lumbar level. J Neuroradiol 22:12–19
Lo D, Vallée JN, Spelle L, Cormier E, Saillant G, Rancurel G, Chiras J (2002) Unusual origin of the artery of Adamkiewicz from the fourth lumbar artery. Neuroradiology 44:153–157
Desproges-Gotteron R (1955) Contribution à l’étude de la sciatique paralysante. Thèse Médecine N°342, Paris
de Sèze S, Guillaume J, Desproges-Gotteron R, Jurmand SH, Maitre M (1957) Sciatique paralysante (Etude clinique, pathogénique, thérapeutique d’après 100 observations). Sem Hôp Paris 28:548–572
Biglioli P, Roberto M, Cannata A, Parolari A, Fumero A, Grillo F, Maggioni M, Coggi G, Spirito R (2004) Upper and lower spinal cord blood supply: the continuity of the anterior spinal artery and the relevance of the lumbar arteries. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 127:1188–1192
Fautrel B, Rozenberg S, Koeger AC, Willer JC, Bourgeois P (1998) L5-S1 disc origin for a pyramidal syndrome? Lancet 352:1679
Balblanc JC, Pretot C, Ziegler F (1998) Vascular complication involving the conus medullaris or cauda equina after vertebral manipulation for an L4-5 disk herniation. Rev Rhum 65:279–282
Tiso RL, Cutler T, Catania JA, Whalen K (2004) Adverse central nervous system sequelae after selective transforaminal block: the role of corticosteroids. Spine J 4:468–474
Hodges SD, Castleberg RL, Miller T, Ward R, Thornburg C (1998) Cervical epidural steroid injection with intrinsic spinal cord damage: two case reports. Spine 23:2137–2140
Brouwers PJ, Kottink EJ, Simon MA, Prevo RL (2001) A cervical anterior spinal artery syndrome after diagnostic blockade of the right C6-nerve root. Pain 91:397–399
Rozin L, Rozin R, Koehler SA, Abdulrezzak S, Ladham S, Mamdouha B, Dominick J, Wecht CH (2003) Death during transforaminal epidural steroid nerve root block (C7) due to perforation of the left vertebral artery. Am J For Med Pathol 24:351–355
Ludwig MA, Burns SP (2005) Spinal cord infarction following cervical transforaminal epidural injection. Spine 30:266–268
Suresh S, Berman J, Connel DA (2007) Cerebellar and brainstem infarction as a complication of CT-guided transforaminal cervical nerve root block. Skeletal Radiol 36:449–452
Okabadejo GO, Talcott MD, Schmidt RE, Sharma A, Patel A, Mackey RB, Guarino AH, Moran CJ, Riew KD (2008) Perils of intravascular methylprednisolone injection into the vertebral artery: an animal study. J Bone Joint Surg (Am) 90:1932–1938
Roques CF, Condouret J, Soleihavoup JP, Croute F (1987) Les corticoïdes pour infiltrations intra-articulaires : éléments de choix (puissance, microcristaux, excipient). Rhumatologie 39:187–194
Francis AF, Chang EL, Haik BG (1996) Particle size and drug interactions of injectable corticosteroids used in ophthalmic practice. Ophthalmology 103:1884–1888
Ross JS, Modic MT, Masaryk TJ, Carter J, Marcus RE, Bohlman H (1989) Assessment of extradural degenerative disease with Gd-DTPA-enhanced MR imaging: correlation with surgical and pathologic findings. Am J Neuroradiol 10:1243–1249
Van Goethem JWM, Parizel PM, Jinkins JR (2002) Review article: MRI of the portoperative lumbar spine. Neuroradiology 44:723–739
Berenstein A, Lasjaunias P (1992) Surgical neuroangiography. Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg, pp 113–118
Link SC, El-Khoury GY, Guilford WB (1998) Percutaneous epidural and nerve root block and percutaneous lumbar sympatholysis. Radiol Clin N Am 36:509–521
Kelekis AD, Somun T, Yilmaz H, Bize P, Brountzos EN, Lovblad K, Ruefenacht D, Martin JB (2005) Interventional spine procedures. Eur J Radiol 55:362–383
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wybier, M., Gaudart, S., Petrover, D. et al. Paraplegia complicating selective steroid injections of the lumbar spine. Report of five cases and review of the literature. Eur Radiol 20, 181–189 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-009-1539-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-009-1539-7