Abstract
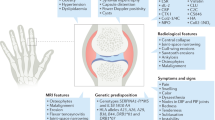
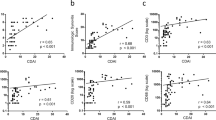
The association between joint damage and disability in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), especially in the later stages of disease, is a main reason why radiographic joint damage is a common and valid outcome measure in RA clinical trials. Most studies have assessed the effect of global joint damage, which has limited our knowledge regarding the individual effects of erosions and cartilage damage on physical function. However, recent data have indicated that joint space narrowing is more closely related to functional status than erosions. Modern imaging techniques that provide improved assessment of the cartilage itself, instead of only joint space narrowing, might help disentangle the separate associations of erosive bone damage and cartilage damage with physical function in patients with RA. The aim of this article is to discuss the current knowledge within this field and the clinical consequences thereof.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scott, D. L., Wolfe, F. & Huizinga, T. W. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 376, 1094–1108 (2010).
Landewé, R. & van der Heijde, D. Presentation and analysis of radiographic data in clinical trials and observational studies. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 64 (Suppl. 4), iv48–iv51 (2005).
US FDA. Guidance for Industry: Clinical Development Programs for Drugs, Devices, and Biological Products for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) [online], (1999).
Østergaard, M., Pedersen, S. J. & Døhn, U. M. Imaging in rheumatoid arthritis—status and recent advances for magnetic resonance imaging, ultrasonography, computed tomography and conventional radiography. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 22, 1019–1044 (2008).
Østergaard, M. et al. OMERACT Rheumatoid Arthritis Magnetic Resonance Imaging Studies. Core set of MRI acquisitions, joint pathology definitions, and the OMERACT RA-MRI scoring system. J. Rheumatol. 30, 1385–1386 (2003).
Bruce, B. & Fries, J. F. The Stanford Health Assessment Questionnaire: dimensions and practical applications. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 1, 20 (2003).
Ware, J. E. Jr & Sherbourne, C. D. The MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36). I. Conceptual framework and item selection. Med. Care 30, 473–483 (1992).
Meenan, R. F., Mason, J. H., Anderson, J. J., Guccione, A. A. & Kazis, L. E. AIMS2. The content and properties of a revised and expanded Arthritis Impact Measurement Scales Health Status Questionnaire. Arthritis Rheum. 35, 1–10 (1992).
Uhlig, T. et al. Reliability of the ICF Core Set for rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 66, 1078–1084 (2007).
Ravindran, V. & Rachapalli, S. An overview of commonly used radiographic scoring methods in rheumatoid arthritis clinical trials. Clin. Rheumatol. 30, 1–6 (2011).
Boini, S. & Guillemin, F. Radiographic scoring methods as outcome measures in rheumatoid arthritis: properties and advantages. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 60, 817–827 (2001).
van der Heijde, D., Dankert, T., Nieman, F., Rau, R. & Boers, M. Reliability and sensitivity to change of a simplification of the Sharp/van der Heijde radiological assessment in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 38, 941–947 (1999).
Østergaard, M. et al. Development and preliminary validation of a magnetic resonance imaging joint space narrowing score for use in rheumatoid arthritis: potential adjunct to the OMERACT RA MRI scoring system. J. Rheumatol. 38, 2045–2050 (2011).
Miese, F. et al. Molecular imaging of cartilage damage of finger joints in early rheumatoid arthritis with delayed Gd(DTPA)2-enhanced MRI. Arthritis Rheum. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/art.33352.
Smolen, J. S. et al. Progression of radiographic joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis: independence of erosions and joint space narrowing. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 68, 1535–1540 (2009).
Scott, D. L. et al. The links between joint damage and disability in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 39, 122–132 (2000).
Ødegård, S. et al. Association of early radiographic damage with impaired physical function in rheumatoid arthritis: a ten-year, longitudinal observational study in 238 patients. Arthritis Rheum. 54, 68–75 (2006).
Smolen, J. S., Aletaha, D., Grisar, J. C., Stamm, T. A. & Sharp, J. T. Estimation of a numerical value for joint damage-related physical disability in rheumatoid arthritis clinical trials. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 69, 1058–1064 (2010).
Smolen, J. S. & Aletaha, D. Patients with rheumatoid arthritis in clinical care. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 63, 221–225 (2004).
Aletaha, D., Smolen, J. & Ward, M. M. Measuring function in rheumatoid arthritis: identifying reversible and irreversible components. Arthritis Rheum. 54, 2784–2792 (2006).
Welsing, P. M., van Gestel, A. M., Swinkels, H. L., Kiemeney, L. A. & van Riel, P. L. The relationship between disease activity, joint destruction, and functional capacity over the course of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 44, 2009–2017 (2001).
van der Heijde, D., Landewé, R., van Vollenhoven, R., Fatenejad, S. & Klareskog, L. Level of radiographic damage and radiographic progression are determinants of physical function: a longitudinal analysis of the TEMPO trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 67, 1267–1270 (2008).
Smolen, J. S., Aletaha, D. & Steiner, G. Does damage cause inflammation? Revisiting the link between joint damage and inflammation. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 68, 159–162 (2009).
van der Heijde, D. Radiographic progression in rheumatoid arthritis: does it reflect outcome? Does it reflect treatment? Ann. Rheum. Dis. 60 (Suppl. 3), iii47–iii50 (2001).
Aletaha, D., Funovits, J. & Smolen, J. S. Physical disability in rheumatoid arthritis is associated with cartilage damage rather than bone destruction. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 70, 733–739 (2011).
Landewé, R. & van der Heijde, D. Joint space narrowing, cartilage and physical function: are we deceived by measurements and distributions? Ann. Rheum. Dis. 70, 717–718 (2011).
Khanna, D. et al. Increased radiographic damage scores at the onset of seropositive rheumatoid arthritis in older patients are associated with osteoarthritis of the hands, but not with more rapid progression of damage. Arthritis Rheum. 52, 2284–2292 (2005).
Slatkowsky-Christensen, B., Mowinckel, P., Loge, J. H. & Kvien, T. K. Health-related quality of life in women with symptomatic hand osteoarthritis: a comparison with rheumatoid arthritis patients, healthy controls, and normative data. Arthritis Rheum. 57, 1404–1409 (2007).
Klareskog, L. et al. Therapeutic effect of the combination of etanercept and methotrexate compared with each treatment alone in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: double-blind randomised controlled trial. Lancet 363, 675–681 (2004).
Smolen, J. S. et al. Radiographic changes in rheumatoid arthritis patients attaining different disease activity states with methotrexate monotherapy and infliximab plus methotrexate: the impacts of remission and tumour necrosis factor blockade. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 68, 823–827 (2009).
Smolen, J. S. et al. Treating rheumatoid arthritis to target: recommendations of an international task force. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 69, 631–637 (2010).
Sharp, J. T. et al. Measurement of joint space width and erosion size. J. Rheumatol. 32, 2456–2461 (2005).
van der Heijde, D. Erosions versus joint space narrowing in rheumatoid arthritis: what do we know? Ann. Rheum. Dis. 70 (Suppl. 1), i116–i118 (2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S. Lillegraven and E. A. Haavardsholm researched data for and wrote the article. All authors contributed to discussing the content and performing review/editing of the manuscript before submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lillegraven, S., van der Heijde, D., Uhlig, T. et al. What is the clinical relevance of erosions and joint space narrowing in RA?. Nat Rev Rheumatol 8, 117–120 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2011.202
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2011.202
This article is cited by
-
Estimation of the global prevalence, incidence, years lived with disability of rheumatoid arthritis in 2019 and forecasted incidence in 2040: results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019
Clinical Rheumatology (2023)
-
The utility of multi-stack alignment and 3D longitudinal image registration to assess bone remodeling in rheumatoid arthritis patients from second generation HR-pQCT scans
BMC Medical Imaging (2020)
-
Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease prevention in rheumatoid arthritis
Nature Reviews Rheumatology (2020)
-
Effects of intra-articular SHINBARO treatment on monosodium iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis in rats
Chinese Medicine (2016)
-
The Burden of Disease in Rheumatoid Arthritis
PharmacoEconomics (2014)