Abstract
Objectives
To evaluate the value of diffusion-weighted MRI (DWI) in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis.
Methods
119 patients with acute appendicitis and 50 controls were enrolled in this prospective study. DWI was obtained with b factors 0, 500 and 1000 s/mm² and were assessed with a visual scoring system by two radiologists followed by quantitative evaluation of the DW images and ADC maps.
Results
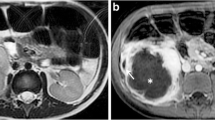
Histopathology revealed appendicitis in 79/92 patients (78%) who had undergone surgery. On visual evaluation, except for one patient with histopathologically proven appendicitis all inflamed appendixes were hyperintense on DWI (98.7%). Quantitative evaluation with DW signal intensities and ADC values revealed a significant difference with normal and inflamed appendixes (p < 0.001). The best discriminative parameter was signal intensity (b 500). With a cut-off value of 56 for the signal intensity the ratio had a sensitivity of 99% and a specificity of 97%. The cut-off ADC value at 1.66 mm²/s had a sensitivity of 97% and a specificity of 99%.
Conclusion
DWI is a valuable technique for the diagnosis of acute appendicitis with both qualitative and quantitative evaluation. DWI increases the conspicuity of the inflamed appendix. We recommend using DWI to diagnose acute appendicitis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown JJ (1991) Acute appendicitis: the radiologist’s role. Radiology 180:13–14
Birnbaum BA, Wilson SR (2000) Appendicitis at the millennium. Radiology 215:337–339
Bongard F, Landers DV, Lewis F (1985) Differential diagnosis of appendicitis and pelvic inflammatory disease. A prospective analysis. Am J Surg 150:90–96
Lau WY, Fan ST, Yiu TF, Chu KW, Wong SH (1984) Negative findings at appendectomy. Am J Surg 148:375–378
Binnebösel M, Otto J, Stumpf M et al (2009) Acute appendicitis. Modern diagnostics—surgical ultrasound. Chirurg 80:579–587
Lally KP, Cox CS Jr, Andrassy RJ (2004) Appendix. In: Townsend CM Jr, Mattox KL, Evers BM et al (eds) Sabiston textbook of surgery, 17th edn. Saunders, New York, pp 1381–1395
Jeffrey RB Jr, Laing FC, Lewis FR (1987) Acute appendicitis: high-resolution real-time US findings. Radiology 163:11–14
Gutierrez CJ, Mariano MC, Faddis DM et al (1999) Doppler ultrasound accurately screens patients with appendicitis. Am Surg 65:1015–1017
Puylaert JB (2003) Ultrasound of the acute abdomen: gastrointestinal conditions. Radiol Clin North Am 41:1227–1242
Simonovsky V (1999) Sonographic detection of normal and abnormal appendix. Clin Radiol 54:533–599
Doria AS, Moineddin R, Kellenberger CJ et al (2006) US or CT for diagnosis of appendicitis in children and adults? A meta-analysis. Radiology 241:83–94
Pedrosa I, Levine D, Eyvazzadeh AD, Siewert B, Ngo L, Rofsky NM (2006) MR imaging evaluation of acute appendicitis in pregnancy. Radiology 238:891–899
Bammer R (2003) Basic principles of diffusion-weighted imaging. Eur J Radiol 45:169–184
Le Bihan D (1990) Diffusion/perfusion MR imaging of the brain: from structure to function. Radiology 177:328–329
Basser PJ, Jones DK (2002) Diffusion tensor MRI: theory, experimental design and data analysis. NMR Biomed 15:456–467
Thoeny HC, De Keyzer F (2007) Extracranial applications of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Eur Radiol 17:1385–1393
Yamashita Y, Tang Y, Takahashi M (1998) Ultrafast MR imaging of the abdomen: echo planar imaging and diffusion-weighted imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 8:367–374
Kwee TC, Takahara T, Ochiai R, Nievelstein RA, Luijten PR (2008) Diffusion-weighted whole-body imaging with background body signal suppression (DWIBS): features and potential applications in oncology. Eur Radiol 18:1937–1952
Kele PG, van der Jagt EJ (2010) Diffusion weighted imaging in the liver. World J Gastroenterol 16:1567–1576
Muraoka N, Uematsu H, Kimura H et al (2008) Apparent diffusion coefficient in pancreatic cancer: characterization and histopathological correlations. J Magn Reson Imaging 27:1302–1308
Albiston E (2002) The role of radiological imaging in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis. Can J Gastroenterol 16:451–463
Forsted DH, Kalbhen CL (2002) CT of pregnant women for urinary tract calculi, pulmonary thromboembolism and acute appendicitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 178:1285
Nitta N, Takahashi M, Furukawa A, Murata K, Mori M, Fukushima M (2005) MR imaging of the normal appendix and acute appendicitis. J Magn Reson Imaging 21:156–165
Hormann M, Paya K, Eibenberger K et al (1998) MR imaging in children with nonperforated acute appendicitis: value of unenhanced MR imaging in sonographically selected cases. AJR Am J Roentgenol 171:467–470
Cobben L, Groot I, Kingma L, Coerkamp E, Puylaert J, Blickman J (2009) A simple MRI protocol in patients with clinically suspected appendicitis: results in 138 patients and effect on outcome of appendectomy. Eur Radiol 19:1175–1183
Takahara T, Imai Y, Yamashita T, Yasuda S, Nasu S, Van Cauteren M (2004) Diffusion weighted whole body imaging with background body signal suppression (DWIBS): technical improvement using free breathing, STIR and high resolution 3D display. Radiat Med 22:275–282
Naganawa S, Sato C, Kumada H et al (2005) Apparent diffusion coefficient in cervical cancer of the uterus: comparison with the normal uterine cervix. Eur Radiol 15:71–78
Tamai K, Koyama T, Saga T et al (2007) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of uterine endometrial cancer. J Magn Reson Imaging 26:682–687
Kilickesmez O, Atilla S, Soylu A et al (2009) Diffusion-weighted imaging of the rectosigmoid colon: preliminary findings. J Comput Assist Tomogr 33:863–866
Oto A, Zhu F, Kulkarni K, Karczmar GS, Turner JR, Rubin D (2009) Evaluation of diffusion-weighted MR imaging for detection of bowel inflammation in patients with Crohn’s disease. Acad Radiol 16:597–603
Kiryu S, Dodanuki K, Takao H et al (2009) Free-breathing diffusion-weighted imaging for the assessment of inflammatory activity in Crohn’s disease. J Magn Reson Imaging 29:880–886
Chan JH, Tsui EY, Luk SH et al (2001) MR diffusion-weighted imaging of kidney: differentiation between hydronephrosis and pyonephrosis. Clin Imaging 25:110–113
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inci, E., Kilickesmez, O., Hocaoglu, E. et al. Utility of diffusion-weighted imaging in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis. Eur Radiol 21, 768–775 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-010-1981-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-010-1981-6