Abstract
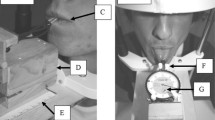
The decreased mouth opening (microstomia) represents a frequent finding in patients with systemic scleroderma (SSD), but little information is available about the efficacy of nonsurgical management of this condition. The aim of this study is to assess the effects of a nonsurgical exercise program on the decreased mouth opening in a group of 10 SSD patients with severe microstomia (maximal mouth opening ≤30 mm). The subjects were instructed to perform an exercise program including both mouth-stretching and oral augmentation exercises. The effects of such exercises were assessed after an 18-week period by measuring the maximal mouth opening of each subject. All patients completed the study and no adverse effects occurred, with the exception of transient muscular fatigue. The exercise program improved the mouth opening of all subjects (mean increase: 10.7±2.06 mm, P<0.005), without significant differences between dentate and edentulous ones (P>0.1). At the end of the 18-week period, all patients commented that eating, speaking and oral hygiene measures were easier. The edentulous subjects also experienced less difficulty inserting their own dentures. These findings suggest that regular application of the proposed exercise program may be useful in the management of microstomia in SSD patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chaffee NR (1998) CREST syndrome: clinical manifestations and dental management. J Prosthod 7:155–160
Dhanasomboon S, Kiattisorn K (2000) Impression procedure for a progressive sclerosis patient: a clinical report. J Prosthet Dent 83:279–282
Ferri C, Valentini G, Cozzi F, Sebastiani M, Nichelassi C, La Montagna G, Bullo A, Cazzato M, Tirri E, Storino F, Giuggioli D, Cuomo G, Rasada M, Bombardieri S, Todesco S, Tirri G (2002) Systemic sclerosis: demographic, clinical, and serologic features and survival in 1,012 Italian patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 81:139–153
Hawk A, English JC (2001) Localized and systemic scleroderma. Semin Cutan Med Surg 20:27–31
Melvin JL (1982) Rheumatic disease-occupational therapy and rehabilitation. F.A. Davis Co., Philadelphia
Nagy G, Kovacs J, Zeher M, Czirjack L (1994) Analysis of the oral manifestations of systemic sclerosis. Oral Surg 77:141–146
Naylor P, Chester WD, Mix E (1984) The nonsurgical treatment of microstomia in scleroderma: a pilot study. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 57:508–511
Paley M, McLoughlin P (1993) Oral problems associated with CREST syndrome: a case report. Br Dent J 175:295–296
Tanturri De Horatio C, Tirri E, Valletta R, Tirri G, Rengo S (2000) L’apertura della bocca in pazienti con sclerosi sistemica: analisi basale e in corso di follow up. Minerva Stomatol 49:409–413
Wood GD, Branco JA (1979) A comparison of three methods of measuring maximal oral opening. J Oral Surg 37:175–177
Acknowledgements
We are indebted to Dr. Salvatore Amato (Operative Unit of Dermatology, A.R.N.A.S. Ospedale Civico e Benfratelli, G. Di Cristina e M. Ascoli, Palermo, Italy) for referral of patients under his care.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00784-003-0243-2
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pizzo, G., Scardina, G.A. & Messina, P. Effects of a nonsurgical exercise program on the decreased mouth opening in patients with systemic scleroderma. Clin Oral Invest 7, 175–178 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-003-0216-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-003-0216-5