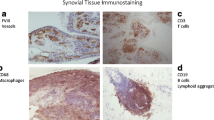
Abstract
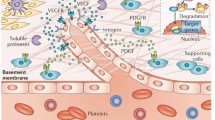
Angiogenesis is the formation of new capillaries from pre-existing vasculature, which plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of several inflammatory autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA), spondyloarthropathies, psoriasis, systemic lupus erythematosus, systemic sclerosis, and atherosclerosis. In RA, excessive migration of circulating leukocytes into the inflamed joint necessitates formation of new blood vessels to provide nutrients and oxygen to the hypertrophic joint. The dominance of the pro-angiogenic factors over the endogenous angiostatic mediators triggers angiogenesis. In this review article, we highlight the underlying mechanisms by which cells present in the RA synovial tissue are modulated to secrete pro-angiogenic factors. We focus on the significance of pro-angiogenic factors such as growth factors, hypoxia-inducible factors, cytokines, chemokines, matrix metalloproteinases, and adhesion molecules on RA pathogenesis. As pro-angiogenic factors are primarily produced from RA synovial tissue macrophages and fibroblasts, we emphasize the key role of RA synovial tissue lining layer in maintaining synovitis through neovascularization. Lastly, we summarize the specific approaches utilized to target angiogenesis. We conclude that the formation of new blood vessels plays an indispensable role in RA progression. However, since the function of several pro-angiogenic mediators is cross regulated, discovering novel approaches to target multiple cascades or selecting an upstream cascade that impairs the activity of a number of pro-angiogenic factors may provide a promising strategy for RA therapy.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Szekanecz Z, Koch AE (2008) Vascular involvement in rheumatic diseases: ‘vascular rheumatology’. Arthritis Res Ther 10(5):224
Szekanecz Z, Koch AE (2007) Mechanisms of disease: angiogenesis in inflammatory diseases. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol 3(11):635–643
Folkman J, Klagsbrun M (1987) Angiogenic factors. Science 235(4787):442–447
Lainer-Carr D, Brahn E (2007) Angiogenesis inhibition as a therapeutic approach for inflammatory synovitis. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol 3(8):434–442
Koch AE (1998) Angiogenesis: implications for rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 41(6):951–962
Veale DJ, Fearon U (2006) Inhibition of angiogenic pathways in rheumatoid arthritis: potential for therapeutic targeting. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 20(5):941–947
Szekanecz Z, Koch AE (2001) Chemokines and angiogenesis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 13(3):202–208
Auerbach W, Auerbach R (1994) Angiogenesis inhibition: a review. Pharmacol Ther 63(3):265–311
Koch AE, Distler O (2007) Vasculopathy and disordered angiogenesis in selected rheumatic diseases: rheumatoid arthritis and systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Res Ther 9(Suppl 2):S3
Chua RA, Arbiser JL (2009) The role of angiogenesis in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Autoimmunity 42(7):574–579
Di Stefano R, Felice F, Balbarini A (2009) Angiogenesis as risk factor for plaque vulnerability. Curr Pharm Des 15(10):1095–1106
Kushner EJ, Bautch VL (2013) Building blood vessels in development and disease. Curr Opin Hematol 20(3):231–236
Szekanecz Z, Koch AE (2005) Endothelial cells in inflammation and angiogenesis. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy 4(3):319–323
Folkman J, Brem H (1992) Angiogenesis and inflammation. In: Gallin JI, Goldstein IM, Snyderman R (eds) Inflammation: basic principles and clinical correlates, 2nd edn. Raven Press, New York, pp 821–839
Folkman J (1997) Angiogenesis and angiogenesis inhibition: an overview. EXS 79:1–8
Folkman J, Shing Y (1992) Angiogenesis. J Biol Chem 267(16):10931–10934
Haringman JJ, Gerlag DM, Zwinderman AH, Smeets TJ, Kraan MC, Baeten D, McInnes IB, Bresnihan B, Tak PP (2005) Synovial tissue macrophages: a sensitive biomarker for response to treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 64(6):834–838
Tak PP, Breedveld FC (1997) Analysis of serial synovial biopsies as a screening method for predicting the effects of therapeutic interventions. J Clin Rheumatol 3(4):186
Tak PP, Bresnihan B (2000) The pathogenesis and prevention of joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis: advances from synovial biopsy and tissue analysis. Arthritis Rheum 43(12):2619–2633
Mulherin D, Fitzgerald O, Bresnihan B (1996) Synovial tissue macrophage populations and articular damage in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 39(1):115–124
Firestein GS (1996) Invasive fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Passive responders or transformed aggressors? Arthritis Rheum 39(11):1781–1790
Gautier EL, Shay T, Miller J, Greter M, Jakubzick C, Ivanov S, Helft J, Chow A, Elpek KG, Gordonov S, Mazloom AR, Ma’ayan A, Chua WJ, Hansen TH, Turley SJ, Merad M, Randolph GJ (2012) Gene-expression profiles and transcriptional regulatory pathways that underlie the identity and diversity of mouse tissue macrophages. Nat Immunol 13(11):1118–1128
Davies LC, Jenkins SJ, Allen JE, Taylor PR (2013) Tissue-resident macrophages. Nat Immunol 14(10):986–995
Tamoutounour S, Henri S, Lelouard H, de Bovis B, de Haar C, van der Woude CJ, Woltman AM, Reyal Y, Bonnet D, Sichien D, Bain CC, Mowat AM, Reis e Sousa C, Poulin LF, Malissen B, Guilliams M (2012) CD64 distinguishes macrophages from dendritic cells in the gut and reveals the Th1-inducing role of mesenteric lymph node macrophages during colitis. Eur J Immunol 42(12):3150–3166
Schulz C, Gomez Perdiguero E, Chorro L, Szabo-Rogers H, Cagnard N, Kierdorf K, Prinz M, Wu B, Jacobsen SE, Pollard JW, Frampton J, Liu KJ, Geissmann F (2012) A lineage of myeloid cells independent of Myb and hematopoietic stem cells. Science 336(6077):86–90
Bain CC, Scott CL, Uronen-Hansson H, Gudjonsson S, Jansson O, Grip O, Guilliams M, Malissen B, Agace WW, Mowat AM (2013) Resident and pro-inflammatory macrophages in the colon represent alternative context-dependent fates of the same Ly6Chi monocyte precursors. Mucosal Immunol 6(3):498–510
Jojic V, Shay T, Sylvia K, Zuk O, Sun X, Kang J, Regev A, Koller D, Best AJ, Knell J, Goldrath A, Joic V, Cohen N, Brennan P, Brenner M, Kim F, Rao TN, Wagers A, Heng T, Ericson J, Rothamel K, Ortiz-Lopez A, Mathis D, Benoist C, Bezman NA, Sun JC, Min-Oo G, Kim CC, Lanier LL, Miller J, Brown B, Merad M, Gautier EL, Jakubzick C, Randolph GJ, Monach P, Blair DA, Dustin ML, Shinton SA, Hardy RR, Laidlaw D, Collins J, Gazit R, Rossi DJ, Malhotra N, Kreslavsky T, Fletcher A, Elpek K, Bellemarte-Pelletier A, Malhotra D, Turley S (2013) Identification of transcriptional regulators in the mouse immune system. Nat Immunol 14(6):633–643
Epelman S, Lavine KJ, Randolph GJ (2014) Origin and functions of tissue macrophages. Immunity 41(1):21–35
Jakubzick C, Gautier EL, Gibbings SL, Sojka DK, Schlitzer A, Johnson TE, Ivanov S, Duan Q, Bala S, Condon T, van Rooijen N, Grainger JR, Belkaid Y, Ma’ayan A, Riches DW, Yokoyama WM, Ginhoux F, Henson PM, Randolph GJ (2013) Minimal differentiation of classical monocytes as they survey steady-state tissues and transport antigen to lymph nodes. Immunity 39(3):599–610
Mills CD (1991) Molecular basis of “suppressor” macrophages. Arginine metabolism via the nitric oxide synthetase pathway. J Immunol 146(8):2719–2723
Mantovani A, Sica A, Sozzani S, Allavena P, Vecchi A, Locati M (2004) The chemokine system in diverse forms of macrophage activation and polarization. Trends Immunol 25(12):677–686
Krausgruber T, Blazek K, Smallie T, Alzabin S, Lockstone H, Sahgal N, Hussell T, Feldmann M, Udalova IA (2011) IRF5 promotes inflammatory macrophage polarization and TH1–TH17 responses. Nat Immunol 12(3):231–238
Mantovani A, Sozzani S, Locati M, Allavena P, Sica A (2002) Macrophage polarization: tumor-associated macrophages as a paradigm for polarized M2 mononuclear phagocytes. Trends Immunol 23(11):549–555
Konisti S, Kiriakidis S, Paleolog EM (2012) Hypoxia—a key regulator of angiogenesis and inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 8(3):153–162
Neumann E, Lefevre S, Zimmermann B, Gay S, Muller-Ladner U (2010) Rheumatoid arthritis progression mediated by activated synovial fibroblasts. Trends Mol Med 16(10):458–468
Bartok B, Firestein GS (2010) Fibroblast-like synoviocytes: key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Rev 233(1):233–255
Pap T, Meinecke I, Muller-Ladner U, Gay S (2005) Are fibroblasts involved in joint destruction? Ann Rheum Dis 64(Suppl 4):iv52–iv54
Huber LC, Distler O, Tarner I, Gay RE, Gay S, Pap T (2006) Synovial fibroblasts: key players in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 45(6):669–675
Niedermeier M, Pap T, Korb A (2010) Therapeutic opportunities in fibroblasts in inflammatory arthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 24(4):527–540
Fava RA, Olsen NJ, Spencer-Green G, Yeo KT, Yeo TK, Berse B, Jackman RW, Senger DR, Dvorak HF, Brown LF (1994) Vascular permeability factor/endothelial growth factor (VPF/VEGF): accumulation and expression in human synovial fluids and rheumatoid synovial tissue. J Exp Med 180:341–346
Szekanecz Z, Koch AE (2007) Macrophages and their products in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 19(3):289–295
Koch AE, Harlow LA, Haines GK, Amento EP, Unemori EN, Wong WL, Pope RM, Ferrara N (1994) Vascular endothelial growth factor. A cytokine modulating endothelial function in rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol 152(8):4149–4156
Brouwer E, Gouw AS, Posthumus MD, van Leeuwen MA, Boerboom AL, Bijzet J, Bos R, Limburg PC, Kallenberg CG, Westra J (2009) Hypoxia inducible factor-1-alpha (HIF-1alpha) is related to both angiogenesis and inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 27(6):945–951
Marrelli A, Cipriani P, Liakouli V, Carubbi F, Perricone C, Perricone R, Giacomelli R (2011) Angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis: a disease specific process or a common response to chronic inflammation? Autoimmun Rev 10(10):595–598
Hu F, Mu R, Zhu J, Shi L, Li Y, Liu X, Shao W, Li G, Li M, Su Y, Cohen PL, Qiu X, Li Z (2014) Hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha provoke toll-like receptor signalling-induced inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 73(5):928–936
Lu J, Kasama T, Kobayashi K, Yoda Y, Shiozawa F, Hanyuda M, Negishi M, Ide H, Adachi M (2000) Vascular endothelial growth factor expression and regulation of murine collagen-induced arthritis. J Immunol 164(11):5922–5927
Cramer T, Yamanishi Y, Clausen BE, Forster I, Pawlinski R, Mackman N, Haase VH, Jaenisch R, Corr M, Nizet V, Firestein GS, Gerber HP, Ferrara N, Johnson RS (2003) HIF-1alpha is essential for myeloid cell-mediated inflammation. Cell 112(5):645–657
Shahrara S, Volin MV, Connors MA, Haines GK, Koch AE (2002) Differential expression of the angiogenic Tie receptor family in arthritic and normal synovial tissue. Arthritis Res 4(3):201–208
Fearon U, Griosios K, Fraser A, Reece R, Emery P, Jones PF, Veale DJ (2003) Angiopoietins, growth factors, and vascular morphology in early arthritis. J Rheumatol 30(2):260–268
Gravallese EM, Pettit AR, Lee R, Madore R, Manning C, Tsay A, Gaspar J, Goldring MB, Goldring SR, Oettgen P (2003) Angiopoietin-1 is expressed in the synovium of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and is induced by tumour necrosis factor alpha. Ann Rheum Dis 62(2):100–107
Clavel G, Bessis N, Boissier MC (2003) Recent data on the role for angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis. Joint Bone Spine 70(5):321–326
Daly C, Eichten A, Castanaro C, Pasnikowski E, Adler A, Lalani AS, Papadopoulos N, Kyle AH, Minchinton AI, Yancopoulos GD, Thurston G (2013) Angiopoietin-2 functions as a Tie2 agonist in tumor models, where it limits the effects of VEGF inhibition. Cancer Res 73(1):108–118
Chen Y, Donnelly E, Kobayashi H, Debusk LM, Lin PC (2005) Gene therapy targeting the Tie2 function ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis and protects against bone destruction. Arthritis Rheum 52(5):1585–1594
Honorati MC, Neri S, Cattini L, Facchini A (2006) Interleukin-17, a regulator of angiogenic factor release by synovial fibroblasts. Osteoarthr Cartil 14(4):345–352
Shibuya H, Yoshitomi H, Murata K, Kobayashi S, Furu M, Ishikawa M, Fujii T, Ito H, Matsuda S (2015) TNFalpha, PDGF, and TGFbeta synergistically induce synovial lining hyperplasia via inducible PI3Kdelta. Mod Rheumatol 25(1):72–78
Koyama K, Hatsushika K, Ando T, Sakuma M, Wako M, Kato R, Haro H, Sugiyama H, Hamada Y, Ogawa H, Nakao A (2007) Imatinib mesylate both prevents and treats the arthritis induced by type II collagen antibody in mice. Mod Rheumatol 17(4):306–310
Kokkonen H, Soderstrom I, Rocklov J, Hallmans G, Lejon K, Rantapaa Dahlqvist S (2010) Up-regulation of cytokines and chemokines predates the onset of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 62(2):383–391
Leibovich SJ, Polverini PJ, Shepard HM, Wiseman DM, Shively V, Nuseir N (1987) Macrophage-induced angiogenesis is mediated by tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Nature 329(6140):630–632
Strunk J, Bundke E, Lange U (2006) Anti-TNF-alpha antibody Infliximab and glucocorticoids reduce serum vascular endothelial growth factor levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a pilot study. Rheumatol Int 26(3):252–256
Markham T, Mullan R, Golden-Mason L, Rogers S, Bresnihan B, Fitzgerald O, Fearon U, Veale DJ (2006) Resolution of endothelial activation and down-regulation of Tie2 receptor in psoriatic skin after infliximab therapy. J Am Acad Dermatol 54(6):1003–1012
Lubberts E (2010) Th17 cytokines and arthritis. Semin Immunopathol 32(1):43–53
Pickens SR, Volin MV, Mandelin AM II, Kolls JK, Pope RM, Shahrara S (2010) IL-17 contributes to angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol 184(6):3233–3241
Pickens SR, Chamberlain ND, Volin MV, Gonzalez M, Pope RM, Mandelin AM II, Kolls JK, Shahrara S (2011) Anti-CXCL5 therapy ameliorates IL-17-induced arthritis by decreasing joint vascularization. Angiogen 14(4):443–455
Chen DY, Chen YM, Chen HH, Hsieh CW, Lin CC, Lan JL (2011) Increasing levels of circulating Th17 cells and interleukin-17 in rheumatoid arthritis patients with an inadequate response to anti-TNF-alpha therapy. Arthritis Res Ther 13(4):R126
Shu Q, Amin MA, Ruth JH, Campbell PL, Koch AE (2012) Suppression of endothelial cell activity by inhibition of TNFalpha. Arthritis Res Ther 14(2):R88
Choe JY, Lee SJ, Park SH, Kim SK (2012) Tacrolimus (FK506) inhibits interleukin-1beta-induced angiopoietin-1, Tie-2 receptor, and vascular endothelial growth factor through down-regulation of JNK and p38 pathway in human rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Joint Bone Spine 79(2):137–143
Pickens SR, Chamberlain ND, Volin MV, Pope RM, Mandelin AM II, Shahrara S (2011) Characterization of CCL19 and CCL21 in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 63(4):914–922
Isozaki T, Arbab AS, Haas CS, Amin MA, Arendt MD, Koch AE, Ruth JH (2013) Evidence that CXCL16 is a potent mediator of angiogenesis and is involved in endothelial progenitor cell chemotaxis: studies in mice with K/BxN serum-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 65(7):1736–1746
Nakae S, Saijo S, Horai R, Sudo K, Mori S, Iwakura Y (2003) IL-17 production from activated T cells is required for the spontaneous development of destructive arthritis in mice deficient in IL-1 receptor antagonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(10):5986–5990
Badolato R, Oppenheim JJ (1996) Role of cytokines, acute-phase proteins, and chemokines in the progression of rheumatoid arthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum 26(2):526–538
Gabay C (2006) Interleukin-6 and chronic inflammation. Arthritis Res Ther 8(Suppl 2):S3
Blue ML, Conrad P, Webb DL, Sarr T, Macaro M (1993) Interacting monocytes and synoviocytes induce adhesion molecules by a cytokine-regulated process. Lymphokine Cytokine Res 12(4):213–218
Nakahara H, Song J, Sugimoto M, Hagihara K, Kishimoto T, Yoshizaki K, Nishimoto N (2003) Anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody therapy reduces vascular endothelial growth factor production in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 48(6):1521–1529
Kayakabe K, Kuroiwa T, Sakurai N, Ikeuchi H, Kadiombo AT, Sakairi T, Matsumoto T, Maeshima A, Hiromura K, Nojima Y (2012) Interleukin-6 promotes destabilized angiogenesis by modulating angiopoietin expression in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 51(9):1571–1579
Ogami K, Yamaguchi R, Imoto S, Tamada Y, Araki H, Print C, Miyano S (2012) Computational gene network analysis reveals TNF-induced angiogenesis. BMC Syst Biol 6(Suppl 2):S12
Chen Z, Kim SJ, Essani AB, Volin MV, Vila OM, Swedler W, Arami S, Volkov S, Sardin LV, Sweiss N, Shahrara S (2014) Characterising the expression and function of CCL28 and its corresponding receptor, CCR10, in RA pathogenesis. Ann Rheum Dis. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204530
Shetty A, Hanson R, Korsten P, Shawagfeh M, Arami S, Volkov S, Vila O, Swedler W, Shunaigat AN, Smadi S, Sawaqed R, Perkins D, Shahrara S, Sweiss NJ (2014) Tocilizumab in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and beyond. Drug Des Dev Ther 8:349–364
Huang Q, Ma Y, Adebayo A, Pope RM (2007) Increased macrophage activation mediated through toll-like receptors in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 56(7):2192–2201
Koch AE, Kunkel SL, Burrows JC, Evanoff HL, Haines GK, Pope RM, Strieter RM (1991) Synovial tissue macrophage as a source of the chemotactic cytokine IL-8. J Immunol 147(7):2187–2195
Cho ML, Ju JH, Kim HR, Oh HJ, Kang CM, Jhun JY, Lee SY, Park MK, Min JK, Park SH, Lee SH, Kim HY (2007) Toll-like receptor 2 ligand mediates the upregulation of angiogenic factor, vascular endothelial growth factor and interleukin-8/CXCL8 in human rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. Immunol Lett 108(2):121–128
Koch AE, Polverini PJ, Kunkel SL, Harlow LA, DiPietro LA, Elner VM, Elner SG, Strieter RM (1992) Interleukin-8 as a macrophage-derived mediator of angiogenesis. Science 258(5089):1798–1801
Mehta VB, Hart J, Wewers MD (2001) ATP-stimulated release of interleukin (IL)-1beta and IL-18 requires priming by lipopolysaccharide and is independent of caspase-1 cleavage. J Biol Chem 276(6):3820–3826
Gracie JA, Forsey RJ, Chan WL, Gilmour A, Leung BP, Greer MR, Kennedy K, Carter R, Wei XQ, Xu D, Field M, Foulis A, Liew FY, McInnes IB (1999) A proinflammatory role for IL-18 in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest 104(10):1393–1401
Moller B, Kessler U, Rehart S, Kalina U, Ottmann OG, Kaltwasser JP, Hoelzer D, Kukoc-Zivojnov N (2002) Expression of interleukin-18 receptor in fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Arthritis Res 4:139–144
Verri WA Jr, Cunha TM, Ferreira SH, Wei X, Leung BP, Fraser A, McInnes IB, Liew FY, Cunha FQ (2007) IL-15 mediates antigen-induced neutrophil migration by triggering IL-18 production. Eur J Immunol 37(12):3373–3380
Marotte H, Ahmed S, Ruth JH, Koch AE (2010) Blocking ERK-1/2 reduces tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced interleukin-18 bioactivity in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts by induction of interleukin-18 binding protein A. Arthritis Rheum 62(3):722–731
Volin MV, Koch AE (2011) Interleukin-18: a mediator of inflammation and angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis. J Interferon Cytokine Res 31(10):745–751
Canetti CA, Leung BP, Culshaw S, McInnes IB, Cunha FQ, Liew FY (2003) IL-18 enhances collagen-induced arthritis by recruiting neutrophils via TNF-alpha and leukotriene B4. J Immunol 171(2):1009–1015
Ruth JH, Park CC, Amin MA, Lesch C, Marotte H, Shahrara S, Koch AE (2010) Interleukin-18 as an in vivo mediator of monocyte recruitment in rodent models of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 12(3):R118
Amin MA, Rabquer BJ, Mansfield PJ, Ruth JH, Marotte H, Haas CS, Reamer EN, Koch AE (2010) Interleukin 18 induces angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo via Src and Jnk kinases. Ann Rheum Dis 69(12):2204–2212
Park CC, Morel JC, Amin MA, Connors MA, Harlow LA, Koch AE (2001) Evidence of IL-18 as a novel angiogenic mediator. J Immunol 167(3):1644–1653
Amin MA, Mansfield PJ, Pakozdi A, Campbell PL, Ahmed S, Martinez RJ, Koch AE (2007) Interleukin-18 induces angiogenic factors in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue fibroblasts via distinct signaling pathways. Arthritis Rheum 56(6):1787–1797
Morel JC, Park CC, Kumar P, Koch AE (2001) Interleukin-18 induces rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblast CXC chemokine production through NFkappaB activation. Lab Invest 81(10):1371–1383
Yoo JK, Kwon H, Khil LY, Zhang L, Jun HS, Yoon JW (2005) IL-18 induces monocyte chemotactic protein-1 production in macrophages through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt and MEK/ERK1/2 pathways. J Immunol 175(12):8280–8286
Onodera S, Tanji H, Suzuki K, Kaneda K, Mizue Y, Sagawa A, Nishihira J (1999) High expression of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in the synovial tissues of rheumatoid joints. Cytokine 11(2):163–167
Leech M, Metz C, Hall P, Hutchinson P, Gianis K, Smith M, Weedon H, Holdsworth SR, Bucala R, Morand EF (1999) Macrophage migration inhibitory factor in rheumatoid arthritis: evidence of proinflammatory function and regulation by glucocorticoids. Arthritis Rheum 42(8):1601–1608
Calandra T, Bernhagen J, Mitchell RA, Bucala R (1994) The macrophage is an important and previously unrecognized source of macrophage migration inhibitory factor. J Exp Med 179(6):1895–1902
Calandra T, Bernhagen J, Metz CN, Spiegel LA, Bacher M, Donnelly T, Cerami A, Bucala R (1995) MIF as a glucocorticoid-induced modulator of cytokine production. Nature 377(6544):68–71
Donnelly SC, Haslett C, Reid PT, Grant IS, Wallace WA, Metz CN, Bruce LJ, Bucala R (1997) Regulatory role for macrophage migration inhibitory factor in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Nat Med 3(3):320–323
Onodera S, Kaneda K, Mizue Y, Koyama Y, Fujinaga M, Nishihira J (2000) Macrophage migration inhibitory factor up-regulates expression of matrix metalloproteinases in synovial fibroblasts of rheumatoid arthritis. J Biol Chem 275(1):444–450
Onodera S, Nishihira J, Koyama Y, Majima T, Aoki Y, Ichiyama H, Ishibashi T, Minami A (2004) Macrophage migration inhibitory factor up-regulates the expression of interleukin-8 messenger RNA in synovial fibroblasts of rheumatoid arthritis patients: common transcriptional regulatory mechanism between interleukin-8 and interleukin-1beta. Arthritis Rheum 50(5):1437–1447
Amin MA, Volpert OV, Woods JM, Kumar P, Harlow LA, Koch AE (2003) Migration inhibitory factor mediates angiogenesis via mitogen-activated protein kinase and phosphatidylinositol kinase. Circ Res 93(4):321–329
Nishihira J, Koyama Y, Mizue Y (1998) Identification of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) in human vascular endothelial cells and its induction by lipopolysaccharide. Cytokine 10(3):199–205
Ogawa H, Nishihira J, Sato Y, Kondo M, Takahashi N, Oshima T, Todo S (2000) An antibody for macrophage migration inhibitory factor suppresses tumour growth and inhibits tumour-associated angiogenesis. Cytokine 12(4):309–314
Leech M, Metz C, Santos L, Peng T, Holdsworth SR, Bucala R, Morand EF (1998) Involvement of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in the evolution of rat adjuvant arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 41(5):910–917
Santos LL, Dacumos A, Yamana J, Sharma L, Morand EF (2008) Reduced arthritis in MIF deficient mice is associated with reduced T cell activation: down-regulation of ERK MAP kinase phosphorylation. Clin Exp Immunol 152(2):372–380
Singh A, Leng L, Fan J, Gajda M, Brauer R, Fingerle-Rowson G, Bucala R, Illges H (2013) Macrophage-derived, macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) is necessary to induce disease in the K/BxN serum-induced model of arthritis. Rheumatol Int 33(9):2301–2308
Szekanecz Z, Vegvari A, Szabo Z, Koch AE (2010) Chemokines and chemokine receptors in arthritis. Front Biosci (Schol Ed) 2:153–167
Maruotti N, Cantatore FP, Crivellato E, Vacca A, Ribatti D (2007) Macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis. Histol Histopathol 22(5):581–586
Asquith DL, Bryce SA, Nibbs RJ (2015) Targeting cell migration in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 27(2):204–211
Park YJ, Kim JY, Park J, Choi JJ, Kim WU, Cho CS (2014) Bone erosion is associated with reduction of circulating endothelial progenitor cells and endothelial dysfunction in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 66(6):1450–1460
Wu PF, Lu ZP, Cai BB, Tian L, Zou C, Jiang KR, Miao Y (2013) Role of CXCL12/CXCR4 signaling axis in pancreatic cancer. Chin Med J 126(17):3371–3374
Wang H, Liu W, Wei D, Hu K, Wu X, Yao Y (2014) Effect of the LPA-mediated CXCL12–CXCR4 axis in the tumor proliferation, migration and invasion of ovarian cancer cell lines. Oncol Lett 7(5):1581–1585
Ghanem I, Riveiro ME, Paradis V, Faivre S, de Parga PM, Raymond E (2014) Insights on the CXCL12-CXCR4 axis in hepatocellular carcinoma carcinogenesis. Am J Transl Res 6(4):340–352
Villalvilla A, Gomez R, Roman-Blas JA, Largo R, Herrero-Beaumont G (2014) SDF-1 signaling: a promising target in rheumatic diseases. Expert Opin Ther Targets 18(9):1077–1087
Pablos JL, Santiago B, Galindo M, Torres C, Brehmer MT, Blanco FJ, Garcia-Lazaro FJ (2003) Synoviocyte-derived CXCL12 is displayed on endothelium and induces angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol 170(4):2147–2152
Tachibana K, Hirota S, Iizasa H, Yoshida H, Kawabata K, Kataoka Y, Kitamura Y, Matsushima K, Yoshida N, Nishikawa S, Kishimoto T, Nagasawa T (1998) The chemokine receptor CXCR4 is essential for vascularization of the gastrointestinal tract. Nature 393(6685):591–594
Blades MC, Ingegnoli F, Wheller SK, Manzo A, Wahid S, Panayi GS, Perretti M, Pitzalis C (2002) Stromal cell-derived factor 1 (CXCL12) induces monocyte migration into human synovium transplanted onto SCID mice. Arthritis Rheum 46(3):824–836
Madge LA, Kluger MS, Orange JS, May MJ (2008) Lymphotoxin-alpha 1 beta 2 and LIGHT induce classical and noncanonical NF-kappa B-dependent proinflammatory gene expression in vascular endothelial cells. J Immunol 180(5):3467–3477
Noort AR, van Zoest KP, Weijers EM, Koolwijk P, Maracle CX, Novack DV, Siemerink MJ, Schlingemann RO, Tak PP, Tas SW (2014) NF-kappaB-inducing kinase is a key regulator of inflammation-induced and tumour-associated angiogenesis. J Pathol 234(3):375–385
Salcedo R, Wasserman K, Young HA, Grimm MC, Howard OM, Anver MR, Kleinman HK, Murphy WJ, Oppenheim JJ (1999) Vascular endothelial growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor induce expression of CXCR4 on human endothelial cells: in vivo neovascularization induced by stromal-derived factor-1alpha. Am J Pathol 154(4):1125–1135
Rempel SA, Dudas S, Ge S, Gutierrez JA (2000) Identification and localization of the cytokine SDF1 and its receptor, CXC chemokine receptor 4, to regions of necrosis and angiogenesis in human glioblastoma. Clin Cancer Res 6(1):102–111
Koshiba T, Hosotani R, Miyamoto Y, Ida J, Tsuji S, Nakajima S, Kawaguchi M, Kobayashi H, Doi R, Hori T, Fujii N, Imamura M (2000) Expression of stromal cell-derived factor 1 and CXCR4 ligand receptor system in pancreatic cancer: a possible role for tumor progression. Clin Cancer Res 6(9):3530–3535
Matthys P, Hatse S, Vermeire K, Wuyts A, Bridger G, Henson GW, De Clercq E, Billiau A, Schols D (2001) AMD3100, a potent and specific antagonist of the stromal cell-derived factor-1 chemokine receptor CXCR4, inhibits autoimmune joint inflammation in IFN-gamma receptor-deficient mice. J Immunol 167(8):4686–4692
Ruth JH, Haas CS, Park CC, Amin MA, Martinez RJ, Haines GK III, Shahrara S, Campbell PL, Koch AE (2006) CXCL16-mediated cell recruitment to rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue and murine lymph nodes is dependent upon the MAPK pathway. Arthritis Rheum 54(3):765–778
Katschke KJ Jr, Rottman JB, Ruth JH, Qin S, Wu L, LaRosa G, Ponath P, Park CC, Pope RM, Koch AE (2001) Differential expression of chemokine receptors on peripheral blood, synovial fluid, and synovial tissue monocytes/macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 44(5):1022–1032
Ruth JH, Rottman JB, Katschke KJ Jr, Qin S, Wu L, LaRosa G, Ponath P, Pope RM, Koch AE (2001) Selective lymphocyte chemokine receptor expression in the rheumatoid joint. Arthritis Rheum 44(12):2750–2760
Shahrara S, Amin MA, Woods JM, Haines GK, Koch AE (2003) Chemokine receptor expression and in vivo signaling pathways in the joints of rats with adjuvant-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 48(12):3568–3583
Shahrara S, Proudfoot AE, Woods JM, Ruth JH, Amin MA, Park CC, Haas CS, Pope RM, Haines GK, Zha YY, Koch AE (2005) Amelioration of rat adjuvant-induced arthritis by Met-RANTES. Arthritis Rheum 52(6):1907–1919
Shahrara S, Proudfoot AE, Park CC, Volin MV, Haines GK, Woods JM, Aikens CH, Handel TM, Pope RM (2008) Inhibition of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 ameliorates rat adjuvant-induced arthritis. J Immunol 180(5):3447–3456
Pickens SR, Chamberlain ND, Volin MV, Pope RM, Talarico NE, Mandelin AM II, Shahrara S (2012) Role of the CCL21 and CCR7 pathways in rheumatoid arthritis angiogenesis. Arthritis Rheum 64(8):2471–2481
Ruth JH, Volin MV, Haines GK III, Woodruff DC, Katschke KJ Jr, Woods JM, Park CC, Morel JC, Koch AE (2001) Fractalkine, a novel chemokine in rheumatoid arthritis and in rat adjuvant-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 44(7):1568–1581
Garcia GE, Xia Y, Chen S, Wang Y, Ye RD, Harrison JK, Bacon KB, Zerwes HG, Feng L (2000) NF-kappaB-dependent fractalkine induction in rat aortic endothelial cells stimulated by IL-1beta, TNF-alpha, and LPS. J Leukoc Biol 67(4):577–584
Imaizumi T, Matsumiya T, Fujimoto K, Okamoto K, Cui X, Ohtaki U, Hidemi Yoshida, Satoh K (2000) Interferon-gamma stimulates the expression of CX3CL1/fractalkine in cultured human endothelial cells. Tohoku J Exp Med 192(2):127–139
Volin MV, Woods JM, Amin MA, Connors MA, Harlow LA, Koch AE (2001) Fractalkine: a novel angiogenic chemokine in rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Pathol 159(4):1521–1530
Murphy G, Knauper V, Atkinson S, Butler G, English W, Hutton M, Stracke J, Clark I (2002) Matrix metalloproteinases in arthritic disease. Arthritis Res 4(Suppl 3):S39–S49
Pap T, Shigeyama Y, Kuchen S, Fernihough JK, Simmen B, Gay RE, Billingham M, Gay S (2000) Differential expression pattern of membrane-type matrix metalloproteinases in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 43(6):1226–1232
Ahrens D, Koch AE, Pope RM, Stein-Picarella M, Niedbala MJ (1996) Expression of matrix metalloproteinase 9 (96-kd gelatinase B) in human rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 39(9):1576–1587
Freemont AJ, Hampson V, Tilman R, Goupille P, Taiwo Y, Hoyland JA (1997) Gene expression of matrix metalloproteinases 1, 3, and 9 by chondrocytes in osteoarthritic human knee articular cartilage is zone and grade specific. Ann Rheum Dis 56(9):542–549
Vincenti MP, Brinckerhoff CE (2002) Transcriptional regulation of collagenase (MMP-1, MMP-13) genes in arthritis: integration of complex signaling pathways for the recruitment of gene-specific transcription factors. Arthritis Res 4:157–164
Brinckerhoff CE, Matrisian LM (2002) Matrix metalloproteinases: a tail of a frog that became a prince. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3(3):207–214
Akhavani MA, Madden L, Buysschaert I, Sivakumar B, Kang N, Paleolog EM (2009) Hypoxia upregulates angiogenesis and synovial cell migration in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 11(3):R64
Burrage PS, Mix KS, Brinckerhoff CE (2006) Matrix metalloproteinases: role in arthritis. Front Biosci 11:529–543
Kim KS, Choi HM, Lee YA, Choi IA, Lee SH, Hong SJ, Yang HI, Yoo MC (2011) Expression levels and association of gelatinases MMP-2 and MMP-9 and collagenases MMP-1 and MMP-13 with VEGF in synovial fluid of patients with arthritis. Rheumatol Int 31(4):543–547
Mengshol JA, Mix KS, Brinckerhoff CE (2002) Matrix metalloproteinases as therapeutic targets in arthritic diseases: bull’s-eye or missing the mark? Arthritis Rheum 46(1):13–20
Rabquer BJ, Pakozdi A, Michel JE, Gujar BS, Haines GK III, Imhof BA, Koch AE (2008) Junctional adhesion molecule C mediates leukocyte adhesion to rheumatoid arthritis synovium. Arthritis Rheum 58(10):3020–3029
Rabquer BJ, Amin MA, Teegala N, Shaheen MK, Tsou PS, Ruth JH, Lesch CA, Imhof BA, Koch AE (2010) Junctional adhesion molecule-C is a soluble mediator of angiogenesis. J Immunol 185(3):1777–1785
Palmer G, Busso N, Aurrand-Lions M, Talabot-Ayer D, Chobaz-Peclat V, Zimmerli C, Hammel P, Imhof BA, Gabay C (2007) Expression and function of junctional adhesion molecule-C in human and experimental arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 9(4):R65
Leinster DA, Colom B, Whiteford JR, Ennis DP, Lockley M, McNeish IA, Aurrand-Lions M, Chavakis T, Imhof BA, Balkwill FR, Nourshargh S (2013) Endothelial cell junctional adhesion molecule C plays a key role in the development of tumors in a murine model of ovarian cancer. FASEB J 27(10):4244–4253
Mojcik CF, Shevach EM (1997) Adhesion molecules: a rheumatologic perspective. Arthritis Rheum 40(6):991–1004
McMurray RW (1996) Adhesion molecules in autoimmune disease. Semin Arthritis Rheum 25(4):215–233
Hosaka S, Shah MR, Pope RM, Koch AE (1996) Soluble forms of P-selectin and intercellular adhesion molecule-3 in synovial fluids. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 78(3):276–282
Koch AE, Shah MR, Harlow LA, Lovis RM, Pope RM (1994) Soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 in arthritis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 71:208–215
Koch AE, Halloran MM, Haskell CJ, Shah MR, Polverini PJ (1995) Angiogenesis mediated by soluble forms of E-selectin and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1. Nature 376(6540):517–519
Schimmer RC, Schrier DJ, Flory CM, Dykens J, Tung DK, Jacobson PB, Friedl HP, Conroy MC, Schimmer BB, Ward PA (1997) Streptococcal cell wall-induced arthritis: requirements for neutrophils, P-selectin, intercellular adhesion molecule-1, and macrophage-inflammatory protein-2. J Immunol 159:4103–4108
Kakimoto K, Nakamura T, Ishii K, Takashi T, Iigou H, Yagita H, Okumura K, Onoue K (1992) The effect of anti-adhesion molecule antibody on the development of collagen-induced arthritis. Cell Immunol 142(2):326–337
Klimiuk PA, Sierakowski S, Latosiewicz R, Cylwik JP, Cylwik B, Skowronski J, Chwiecko J (2002) Soluble adhesion molecules (ICAM-1, VCAM-1, and E-selectin) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in patients with distinct variants of rheumatoid synovitis. Ann Rheum Dis 61(9):804–809
Shahrara S, Huang Q, Mandelin AM II, Pope RM (2008) TH-17 cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 10(4):R93
Kim SJ, Chen Z, Chamberlain ND, Volin MV, Swedler W, Volkov S, Sweiss N, Shahrara S (2013) Angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis is fostered directly by Toll-like receptor 5 ligation and indirectly through interleukin-17 induction. Arthritis Rheum 65(8):2024–2036
Pickens SR, Chamberlain ND, Volin MV, Mandelin AM II, Agrawal H, Matsui M, Yoshimoto T, Shahrara S (2011) Local expression of interleukin-27 ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 63(8):2289–2298
Springer TA (1994) Traffic signals for lymphocyte recirculation and leukocyte emigration: the multistep paradigm. Cell 76(2):301–314
Lasky LA (1992) Selectins: interpreters of cell-specific carbohydrate information during inflammation. Science 258(5084):964–969
Bevilacqua MP, Stengelin S, Gimbrone MA Jr, Seed B (1989) Endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule 1: an inducible receptor for neutrophils related to complement regulatory proteins and lectins. Science 243(4895):1160–1165
Maruotti N, Cantatore FP, Ribatti D (2014) Putative effects of potentially anti-angiogenic drugs in rheumatic diseases. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 70(2):135–140
Lubberts E, Koenders MI, Oppers-Walgreen B, van den Bersselaar L, Coenen-de Roo CJ, Joosten LA, van den Berg WB (2004) Treatment with a neutralizing anti-murine interleukin-17 antibody after the onset of collagen-induced arthritis reduces joint inflammation, cartilage destruction, and bone erosion. Arthritis Rheum 50(2):650–659
Genovese MC, Durez P, Richards HB, Supronik J, Dokoupilova E, Mazurov V, Aelion JA, Lee SH, Codding CE, Kellner H, Ikawa T, Hugot S, Mpofu S (2013) Efficacy and safety of secukinumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a phase II, dose-finding, double-blind, randomised, placebo controlled study. Ann Rheum Dis 72(6):863–869
Genovese MC, Greenwald M, Cho CS, Berman A, Jin L, Cameron GS, Benichou O, Xie L, Braun D, Berclaz PY, Banerjee S (2014) A phase II randomized study of subcutaneous ixekizumab, an anti-interleukin-17 monoclonal antibody, in rheumatoid arthritis patients who were naive to biologic agents or had an inadequate response to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors. Arthritis Rheumatol 66(7):1693–1704
Mease PJ, Genovese MC, Greenwald MW, Ritchlin CT, Beaulieu AD, Deodhar A, Newmark R, Feng J, Erondu N, Nirula A (2014) Brodalumab, an anti-IL17RA monoclonal antibody, in psoriatic arthritis. N Engl J Med 370(24):2295–2306
Yao HP, Qian Y, Shao XT, Xu ZR, Cheng LF, Feng L, Wu NP, Yang YM (2010) Construction of a recombinant adenovirus vector expressing IL-18BP/IL-4 fusion gene and the anti-inflammatory effect induced by this gene on lipopolysaccharide-stimulated synovial fibroblasts. Inflamm Res 59(2):97–104
Mistry P, Reid J, Pouliquen I, McHugh S, Abberley L, DeWall S, Taylor A, Tong X, Rocha Del Cura M, McKie E (2014) Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of single-dose antiinterleukin-18 mAb GSK1070806 in healthy and obese subjects. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 52(10):867–879
Tak PP, Bacchi M, Bertolino M (2006) Pharmacokinetics of IL-18 binding protein in healthy volunteers and subjects with rheumatoid arthritis or plaque psoriasis. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 31(2):109–116
Greven D, Leng L, Bucala R (2010) Autoimmune diseases: MIF as a therapeutic target. Expert Opin Ther Targets 14(3):253–264
Cournia Z, Leng L, Gandavadi S, Du X, Bucala R, Jorgensen WL (2009) Discovery of human macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF)-CD74 antagonists via virtual screening. J Med Chem 52(2):416–424
Fruehauf S (2013) Current clinical indications for plerixafor. Transfus Med Hemother 40(4):246–250
Kuhne MR, Mulvey T, Belanger B, Chen S, Pan C, Chong C, Cao F, Niekro W, Kempe T, Henning KA, Cohen LJ, Korman AJ, Cardarelli PM (2013) BMS-936564/MDX-1338: a fully human anti-CXCR4 antibody induces apoptosis in vitro and shows antitumor activity in vivo in hematologic malignancies. Clin Cancer Res 19(2):357–366
Coxon A, Bready J, Min H, Kaufman S, Leal J, Yu D, Lee TA, Sun JR, Estrada J, Bolon B, McCabe J, Wang L, Rex K, Caenepeel S, Hughes P, Cordover D, Kim H, Han SJ, Michaels ML, Hsu E, Shimamoto G, Cattley R, Hurh E, Nguyen L, Wang SX, Ndifor A, Hayward IJ, Falcon BL, McDonald DM, Li L, Boone T, Kendall R, Radinsky R, Oliner JD (2010) Context-dependent role of angiopoietin-1 inhibition in the suppression of angiogenesis and tumor growth: implications for AMG 386, an angiopoietin-1/2-neutralizing peptibody. Mol Cancer Ther 9(10):2641–2651
Weeraratne DK, Lofgren J, Dinnogen S, Swanson SJ, Zhong ZD (2013) Development of a biosensor-based immunogenicity assay capable of blocking soluble drug target interference. J Immunol Methods 396(1–2):44–55
Hah YS, Koh YJ, Lim HS, Kim HO, Cheon YH, Noh HS, Jang KY, Lee SY, Lee GM, Koh GY, Lee SI (2013) Double-antiangiogenic protein DAAP targeting vascular endothelial growth factor A and angiopoietins attenuates collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 15(4):R85
Dorman G, Cseh S, Hajdu I, Barna L, Konya D, Kupai K, Kovacs L, Ferdinandy P (2010) Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors: a critical appraisal of design principles and proposed therapeutic utility. Drugs 70(8):949–964
Thabet MM, Huizinga TW (2006) Drug evaluation: apratastat, a novel TACE/MMP inhibitor for rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 7(11):1014–1019
Gordon KB, Papp KA, Hamilton TK, Walicke PA, Dummer W, Li N, Bresnahan BW, Menter A (2003) Efalizumab for patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 290(23):3073–3080
Prater EF, Day A, Patel M, Menter A (2014) A retrospective analysis of 72 patients on prior efalizumab subsequent to the time of voluntary market withdrawal in 2009. J Drugs Dermatol 13(6):712–718
Jones R (2000) Rovelizumab (ICOS Corp). IDrugs Investig Drugs J 3(4):442–446
Kavanaugh AF, Davis LS, Nichols LA, Norris SH, Rothlein R, Scharschmidt LA, Lipsky PE (1994) Treatment of refractory rheumatoid arthritis with a monoclonal antibody to intercellular adhesion molecule 1. Arthritis Rheum 37(7):992–999
Kavanaugh AF, Davis LS, Jain RI, Nichols LA, Norris SH, Lipsky PE (1996) A phase I/II open label study of the safety and efficacy of an anti-ICAM-1 (intercellular adhesion molecule-1; CD54) monoclonal antibody in early rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 23(8):1338–1344
Kavanaugh AF, Schulze-Koops H, Davis LS, Lipsky PE (1997) Repeat treatment of rheumatoid arthritis patients with a murine anti-intercellular adhesion molecule 1 monoclonal antibody. Arthritis Rheum 40(5):849–853
Pucci E, Giuliani G, Solari A, Simi S, Minozzi S, Di Pietrantonj C, Galea I (2011) Natalizumab for relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 10:CD007621
Podar K, Zimmerhackl A, Fulciniti M, Tonon G, Hainz U, Tai YT, Vallet S, Halama N, Jager D, Olson DL, Sattler M, Chauhan D, Anderson KC (2011) The selective adhesion molecule inhibitor Natalizumab decreases multiple myeloma cell growth in the bone marrow microenvironment: therapeutic implications. Br J Haematol 155(4):438–448
Mitroulis I, Alexaki VI, Kourtzelis I, Ziogas A, Hajishengallis G, Chavakis T (2015) Leukocyte integrins: role in leukocyte recruitment and as therapeutic targets in inflammatory disease. Pharmacol Ther 147:123–135
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by awards from the National Institutes of Health AR056099 and AR065778, funding provided by Department of Defense PR093477 and Arthritis Foundation Innovative Research Grant. We apologize to colleagues whose studies were not cited because of space limitation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elshabrawy, H.A., Chen, Z., Volin, M.V. et al. The pathogenic role of angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis. Angiogenesis 18, 433–448 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-015-9477-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-015-9477-2