Summary
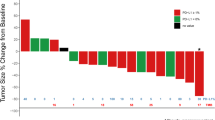
Background Advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients were treated as part of a Phase I dose escalation and expansion study evaluating a true human monoclonal antibody targeting IL-1α (Xilonix), which is intended to modulate the malignant phenotype—inhibiting tumor growth, spread and offering relief of symptoms. Methods Sixteen NSCLC patients were included. Patients failed a median of 4 chemotherapy regimens, including 10/16 failing anti-EGFR therapy. Disease progression was evaluated using a multi-modal approach: tumor response, patient reported outcomes (EORTC-QLQC30), and lean body mass (LBM). Patients received infusions every 2 or 3 weeks until progression, and were followed 24 months to assess survival. Results There were no infusion reactions, dose-limiting toxicities, or deaths due to therapy. Albeit not statistically significant, there was a trend in IL-6 (−2.6 ± 18.5 (0.1 [−2.8–2.4]), platelet counts (−11 ± 54 (−4[−36.0–1.0]), CRP (−3.3 ± 30.2 (0.4 [−10.7–1.8]) and LBM (1.0 ± 2.5 (0.4 [−0.5–2.6]). Self-reported outcomes revealed reductions in pain, fatigue and improvement in appetite. Median survival was 7.6 (IQR 4.4–11.5) months, stratification based on prior anti-EGFR therapy revealed a median survival of 9.4 months (IQR 7.6–12.5) for those pretreated (N = 10) versus a survival of 4.8 months (IQR 4.3–5.7) for those without (N = 6, logrank p = 0.187). Conclusion Xilonix was well tolerated, with gains in LBM and improvement in symptoms suggesting a clinically important response. Although not statistically significant, the survival outcomes observed for patients with and without prior anti-EGFR therapy raises intriguing questions about the potential synergy of IL-1α blockade and anti-EGFR therapy. Further study for this agent in NSCLC is warranted.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A (2014) Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 62:10–29
Thornton et al (2010) Platelet interleukin-1a drives cerebrovascular inflammation. Blood 115(17):3632–3639
Sabrkhany et al (2011) The role of blood platelets in tumor angiogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1815:189–196
Tjomsland V et al (2011) Interleukin 1α sustains the expression of inflammatory factors in human pancreatic cancer microenvironment by targeting cancer-associated fibroblasts. Neoplasia 13(8):664–675
Tomimatsu S, Ichikura T, Mochizuki H (2001) Significant correlation between expression of interleukin-1alpha and liver metastasis in gastric carcinoma. Cancer 91(7):1272–1276
Singer CF et al (2003) Interleukin 1 system and sex steroid receptor expression in human breast cancer: interleukin 1alpha protein secretion is correlated with malignant phenotype. Clin Cancer Res 9(13):4877–4883
Garlanda C, Dinarello CA, Mantovani A (2013) The interleukin-1 family: back to the future. Immunity 39(6):1003–1018. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2013.11.010
Dinarello CA, Simon A, van der Meer JW (2012) Treating inflammation by blocking interleukin-1 in a broad spectrum of diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov 11(8):633–652
Salven et al (2002) Interleukin-1α promotes angiogenesis in vivo via VEGFR-2 pathway by inducing inflammatory cell VEGF synthesis and secretion. FASEB J 16:1471–1473
Van Lint P, Libert C (2007) Chemokine and cytokine processing by matrix metalloproteinases and its effect on leukocyte migration and inflammation. J Leukoc Biol 82(6):1375–1381
Rock KL et al (2010) The sterile inflammatory response. Annu Rev Immunol 28:321–342
Allavena P, Mantovani A (2012) Immunology in the clinic review series; focus on cancer: tumour-associated macrophages: undisputed stars of the inflammatory tumour microenvironment. Clin Exp Immunol 167(2):195–205. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2249.2011.04515.x
Dinarello CA (2014) Interleukin-1α neutralisation in patients with cancer. Lancet Oncol 15(6):552–553. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70164-0
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J et al (2009) New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer 45(2):228–247. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2008.10.026
Wolchok JD et al (2009) Guidelines for the evaluation of immune therapy activity in solid tumors: immune-related response criteria. Clin Cancer Res 15:7412–7420
Quinten C et al (2009) Baseline quality of life as a prognostic indicator of survival: a meta-analysis of individual patient data from EORTC clinical trials. Lancet Oncol 10:865–871
Hong DS et al (2014) MABp1, a first-in-class true human antibody targeting interleukin-1α in refractory cancers: an open-label, phase 1 dose-escalation and expansion study. Lancet Oncol 15(6):656–666
Yeh KY, Li YY, Hsieh LL et al (2010) Analysis of the effect of serum interleukin-6 (IL-6) and soluble IL-6 receptor levels on survival of patients with colorectal cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol 40(6):580–587. doi:10.1093/jjco/hyq010
Stone RL, Nick AM, McNeish IA et al (2012) Paraneoplastic thrombocytosis in ovarian cancer. N Engl J Med 366(7):610–618. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1110352
Ravasco P, Monteiro-Grillo I, Camilo M (2007) Colorectal cancer: intrinsic characteristics modulate cancer energy expenditure and the risk of cachexia. Cancer Invest 25(5):308–314
Quinten C, Coens C, Mauer M et al (2009) Baseline quality of life as a prognostic indicator of survival: a meta-analysis of individual patient data from EORTC clinical trials. Lancet Oncol 10(9):865–871. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70200-1
Herrmann F et al (2004) HER-2/neu-mediated regulation of components of the MHC class I antigen-processing pathway. Cancer Res 64:215–220
Mimura K (2004) T. et al. T cell recognition of HLA-A2 restricted tumor antigens is impaired by the oncogene HER2. Int J Cancer 128:390–401
So T et al (2005) Haplotype loss of HLA class I antigen as an escape mechanism from immune attack in lung cancer. Cancer Res 65(13):5945–5952
Corthay A (2014) Does the immune system naturally protect against cancer? Front Immunol 5:197. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2014.00197. eCollection 2014
Campoli M, Ferrone S (2008) HLA antigen changes in malignant cells: epigenetic mechanisms and biologic significance. Oncogene 27:5869–5885. doi:10.1038/onc.2008.273
Trivedi S, Concha-Benavente F, Srivastava RM, Jie HB, Gibson SP, Schmitt NC, Ferris RL (2014) Immune biomarkers of anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody therapy. Ann Oncol
Pollack BP, Sapkota B, Cartee TV (2011) Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition augments the expression of MHC class I and II genes. Clin Cancer Res 17:4400–4413
Voronov E, Carmi Y, Apte RN (2014) The role IL-1 in tumor-mediated angiogenesis. Front Physiol 5:114. doi:10.3389/fphys.2014.00114, eCollection 2014
Ostrand-Rosenberg S, Sinha P (2009) Myeloid-derived suppressor cells: linking inflammation and cancer. J Immunol 182(8):4499–4506. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0802740
Kim B et al (2013) The interleukin-1α precursor is biologically active and is likely a key alarmin in the IL-1 family of cytokines. Front Immunol 4:391. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2013.00391. eCollection 2013
Fletcher EV et al (2013) EGFR inhibition induces proinflammatory cytokines via NOX4 in HNSCC. Mol Cancer Res 11(12):1574–1584. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-13-0187
Giles KM et al (2013) Axl mediates acquired resistance of head and neck cancer cells to the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor erlotinib. Mol Cancer Ther 12(11):2541–2558. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0170
Stone RL et al (2012) Paraneoplastic thrombocytosis in ovarian cancer. N Engl J Med 366:610–618
Narsale AA, Carson JA (2014) Role of interleukin-6 in cachexia: therapeutic implications. Curr Opin Support Palliat Care 8(4):321–327. doi:10.1097/SPC.0000000000000091
Yao Z et al (2010) TGF-beta IL-6 axis mediates selective and adaptive mechanisms of resistance to molecular targeted therapy in lung cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(35):15535–15540. doi:10.1073/pnas.1009472107
Li L et al (2014) Metformin sensitizes EGFR-TKI-resistant human lung cancer cells in vitro and in vivo through inhibition of IL-6 signaling and EMT reversal. Clin Cancer Res 20(10):2714–2726. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-2613
Qin Y, Ekmekcioglu S, Liu P, Duncan LM, Lizée G, Poindexter N, Grimm EA (2011) Constitutive aberrant endogenous interleukin-1 facilitates inflammation and growth in human melanoma. Mol Cancer Res 9(11):1537–1550. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-11-0279
Compliance with ethical standards
Funding
This study was funded by XBiotech USA, Inc.
Conflicts of interest
DSH reports grants from Xbiotech during the conduct of the study.
RK reports funding for research.
MS and PM are employees of XBiotech with stock options. JS is an employee of XBiotech with stock options, and patents related to anti-IL-1α therapy.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
One sentence summary
IL-1α blockade may help overcome resistance to anti-EGFR therapy by inhibiting the immunosuppressive effects of tumor-associated inflammation.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Materials and Methods S1
EORTC Questionnaire (DOC 39 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, D.S., Janku, F., Naing, A. et al. Xilonix, a novel true human antibody targeting the inflammatory cytokine interleukin-1 alpha, in non-small cell lung cancer. Invest New Drugs 33, 621–631 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-015-0226-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-015-0226-6