Abstract
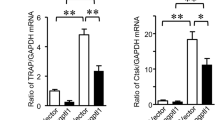
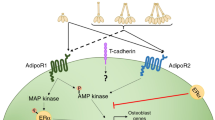
To explore the effects of adiponectin on the bone metabolism in vivo. Bone mineral density (BMD), bone microstructure, serum adiponectin levels, and biochemical markers of the bone turnover were measured in 12-week-old male Adipo−/− and WT mice. In addition, the osteoclast formation, osteoprotegerin (OPG), and the receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand (RANKL) expression were examined. The serum adiponectin levels were normal in the WT mice while undetectable in the Adipo−/− mice. Compared with the WT mice, the Adipo−/− mice had higher BMD, more trabecular bone, greater bone volume fraction, and trabecular thickness in the left femur. On the contrary, fewer osteoclasts were observed in the Adipo−/− mice when compared with the WT mice. Meanwhile, the Adipo−/− mice had a significantly decreased serum carboxyl-terminal telopeptide of type 1 collagen (CTX)/osteocalcin (OC) ratio. Interestingly, both the adiponectin and RANKL would cause a significant increase of CTX/OC ratio in the co-culture of the CD14+ peripheral blood mononuclear cells and the osteoblasts from Adipo−/− mice. Further, immunohistochemistry assays in tibias and both the RT-PCR and immunoblot analyses in the cultured osteoblasts showed the Adipo−/− mice expressed lower levels of RANKL but higher levels of OPG. Adiponectin had a negative effect on the bone metabolism, and this negative effect might be mediated, at least in part, by the OPG/RANKL pathway.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
P.E. Scherer, S. Williams, M. Fogliano, G. Baldini, H.F. Lodish, A novel serum protein similar to C1q, produced exclusively in adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 270(45), 26746–26749 (1995)
K. Maeda, K. Okubo, I. Shimomura, T. Funahashi, Y. Matsuzawa, K. Matsubara, cDNA cloning and expression of a novel adipose specific collagen-like factor, apM1 (AdiPose most abundant gene transcript 1). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 221(2), 286–289 (1996)
Y. Nakano, T. Tobe, N.H. Choi-Miura, T. Mazda, M. Tomita, Isolation and characterization of GBP28, a novel gelatin-binding protein purified from human plasma. J. Biochem. 120(4), 803–812 (1996)
T. Yamauchi, J. Kamon, Y. Ito, A. Tsuchida, T. Yokomizo, S. Kita, T. Sugiyama, M. Miyagishi, K. Hara, M. Tsunoda, K. Murakami, T. Ohteki, S. Uchida, S. Takekawa, H. Waki, N.H. Tsuno, Y. Shibata, Y. Terauchi, P. Froguel, K. Tobe, S. Koyasu, K. Taira, T. Kitamura, T. Shimizu, R. Nagai, T. Kadowaki, Cloning of adiponectin receptors that mediate antidiabetic metabolic effects. Nature 423(6941), 762–769 (2003)
T.P. Combs, A.H. Berg, S. Obici, P.E. Scherer, L. Rossetti, Endogenous glucose production is inhibited by the adipose-derived protein Acrp30. J. Clin. Invest. 108(12), 1875–1881 (2001)
J. Fruebis, T.S. Tsao, S. Javorschi, D. Ebbets-Reed, M.R. Erickson, F.T. Yen, B.E. Bihain, H.F. Lodish, Proteolytic cleavage product of 30-kDa adipocyte complement-related protein increases fatty acid oxidation in muscle and causes weight loss in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98(4), 2005–2010 (2001)
T. Yamauchi, J. Kamon, Y. Minokoshi, Y. Ito, H. Waki, S. Uchida, S. Yamashita, M. Noda, S. Kita, K. Ueki, K. Eto, Y. Akanuma, P. Froguel, F. Foufelle, P. Ferre, D. Carling, S. Kimura, R. Nagai, B.B. Kahn, T. Kadowaki, Adiponectin stimulates glucose utilization and fatty-acid oxidation by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Nat. Med. 8(11), 1288–1295 (2002)
K. Brochu-Gaudreau, C. Rehfeldt, R. Blouin, V. Bordignon, B.D. Murphy, M.F. Palin, Adiponectin action from head to toe. Endocrine 37(1), 11–32 (2010)
H.S. Berner, S.P. Lyngstadaas, A. Spahr, M. Monjo, L. Thommesen, C.A. Drevon, U. Syversen, J.E. Reseland, Adiponectin and its receptors are expressed in bone-forming cells. Bone 35(4), 842–849 (2004)
K.N. Ealey, J. Kaludjerovic, M.C. Archer, W.E. Ward, Adiponectin is a negative regulator of bone mineral and bone strength in growing mice. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 233(12), 1546–1553 (2008)
G.A. Williams, Y. Wang, K.E. Callon, M. Watson, J.M. Lin, J.B. Lam, J.L. Costa, A. Orpe, N. Broom, D. Naot, I.R. Reid, J. Cornish, In vitro and in vivo effects of adiponectin on bone. Endocrinology 150(8), 3603–3610 (2009)
J. Jurimae, T. Jurimae, Plasma adiponectin concentration in healthy pre- and postmenopausal women: relationship with body composition, bone mineral, and metabolic variables. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 293(1), E42–E47 (2007)
X.D. Peng, H. Xie, Q. Zhao, X.P. Wu, Z.Q. Sun, E.Y. Liao, Relationships between serum adiponectin, leptin, resistin, visfatin levels and bone mineral density, and bone biochemical markers in Chinese men. Clin. Chim. Acta 387(1–2), 31–35 (2008)
B. Bozic, G. Loncar, N. Prodanovic, Z. Radojicic, V. Cvorovic, S. Dimkovic, V. Popovic-Brkic, Relationship between high circulating adiponectin with bone mineral density and bone metabolism in elderly males with chronic heart failure. J. Card Fail. 16(4), 301–307 (2010)
L. Basurto, R. Galvan, N. Cordova, R. Saucedo, C. Vargas, S. Campos, E. Halley, F. Avelar, A. Zarate, Adiponectin is associated with low bone mineral density in elderly men. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 160(2), 289–293 (2009)
X.H. Luo, L.J. Guo, L.Q. Yuan, H. Xie, H.D. Zhou, X.P. Wu, E.Y. Liao, Adiponectin stimulates human osteoblasts proliferation and differentiation via the MAPK signaling pathway. Exp. Cell Res. 309(1), 99–109 (2005)
H.W. Lee, S.Y. Kim, A.Y. Kim, E.J. Lee, J.Y. Choi, J.B. Kim, Adiponectin stimulates osteoblast differentiation through induction of COX2 in mesenchymal progenitor cells. Stem Cells 27(9), 2254–2262 (2009)
N. Yamaguchi, T. Kukita, Y.J. Li, J.G. Martinez Argueta, T. Saito, S. Hanazawa, Y. Yamashita, Adiponectin inhibits osteoclast formation stimulated by lipopolysaccharide from Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 49(1), 28–34 (2007)
K. Oshima, A. Nampei, M. Matsuda, M. Iwaki, A. Fukuhara, J. Hashimoto, H. Yoshikawa, I. Shimomura, Adiponectin increases bone mass by suppressing osteoclast and activating osteoblast. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 331(2), 520–526 (2005)
X.H. Luo, L.J. Guo, H. Xie, L.Q. Yuan, X.P. Wu, H.D. Zhou, E.Y. Liao, Adiponectin stimulates RANKL and inhibits OPG expression in human osteoblasts through the MAPK signaling pathway. J. Bone Miner. Res. 21(10), 1648–1656 (2006)
S. Khosla, Minireview: the OPG/RANKL/RANK system. Endocrinology 142(12), 5050–5055 (2001)
Q.P. Wang, L. Yang, X.P. Li, H. Xie, E.Y. Liao, M. Wang, X.H. Luo, Effects of 17beta-estradiol on adiponectin regulation of the expression of osteoprotegerin and receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB ligand. Bone 51(3), 515–523 (2012)
A. Geldyyev, N. Koleganova, G. Piecha, H. Sueltmann, K. Finis, M. Ruschaupt, A. Poustka, M.L. Gross, I. Berger, High expression level of bone degrading proteins as a possible inducer of osteolytic features in pigmented villonodular synovitis. Cancer Lett. 255(2), 275–283 (2007)
G. Musso, Non-alcoholic fatty liver, adipose tissue, and the bone: a new triumvirate on the block. Endocrine 42(2), 237–239 (2012)
H. Zhang, X. Chai, S. Li, Z. Zhang, L. Yuan, H. Xie, H. Zhou, X. Wu, Z. Sheng, E. Liao, Age-related changes in body composition and their relationship with bone mineral density decreasing rates in central south Chinese postmenopausal women. Endocrine 43(3), 643–650 (2013)
H. Li, H. Xie, W. Liu, R. Hu, B. Huang, Y.F. Tan, K. Xu, Z.F. Sheng, H.D. Zhou, X.P. Wu, X.H. Luo, A novel microRNA targeting HDAC5 regulates osteoblast differentiation in mice and contributes to primary osteoporosis in humans. J. Clin. Invest. 119(12), 3666–3677 (2009)
P. Cheng, C. Chen, H.B. He, R. Hu, H.D. Zhou, H. Xie, W. Zhu, R.C. Dai, X.P. Wu, E.Y. Liao, X.H. Luo, miR-148a regulates osteoclastogenesis by targeting V-maf musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene homolog B. J. Bone Miner. Res. 28(5), 1180–1190 (2013)
K. Agbaht, A. Gurlek, J. Karakaya, M. Bayraktar, Circulating adiponectin represents a biomarker of the association between adiposity and bone mineral density. Endocrine 35(3), 371–379 (2009)
L. Lenchik, T.C. Register, F.C. Hsu, K. Lohman, B.J. Nicklas, B.I. Freedman, C.D. Langefeld, J.J. Carr, D.W. Bowden, Adiponectin as a novel determinant of bone mineral density and visceral fat. Bone 33(4), 646–651 (2003)
J.B. Richards, A.M. Valdes, K. Burling, U.C. Perks, T.D. Spector, Serum adiponectin and bone mineral density in women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 92(4), 1517–1523 (2007)
E. Biver, C. Salliot, C. Combescure, L. Gossec, P. Hardouin, I. Legroux-Gerot, B. Cortet, Influence of adipokines and ghrelin on bone mineral density and fracture risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 96(9), 2703–2713 (2011)
P. Szulc, P.D. Delmas, Biochemical markers of bone turnover: potential use in the investigation and management of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Osteoporos. Int. 19(12), 1683–1704 (2008)
S.L. Teitelbaum, Bone resorption by osteoclasts. Science 289(5484), 1504–1508 (2000)
J.M. Blair, H. Zhou, M.J. Seibel, C.R. Dunstan, Mechanisms of disease: roles of OPG, RANKL and RANK in the pathophysiology of skeletal metastasis. Nat. Clin. Pract. Oncol. 3(1), 41–49 (2006)
L.C. Hofbauer, C.A. Kuhne, V. Viereck, The OPG/RANKL/RANK system in metabolic bone diseases. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 4(3), 268–275 (2004)
A. Rogers, R. Eastell, Circulating osteoprotegerin and receptor activator for nuclear factor kappaB ligand: clinical utility in metabolic bone disease assessment. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 90(11), 6323–6331 (2005)
E.M. Lewiecki, RANK ligand inhibition with denosumab for the management of osteoporosis. Expert. Opin. Biol. Ther. 6(10), 1041–1050 (2006)
G. Schett, S. Hayer, J. Zwerina, K. Redlich, J.S. Smolen, Mechanisms of disease: the link between RANKL and arthritic bone disease. Nat. Clin. Pract. Rheumatol. 1(1), 47–54 (2005)
S. Kudlacek, B. Schneider, W. Woloszczuk, P. Pietschmann, R. Willvonseder, Serum levels of osteoprotegerin increase with age in a healthy adult population. Bone 32(6), 681–686 (2003)
Y. Shinoda, M. Yamaguchi, N. Ogata, T. Akune, N. Kubota, T. Yamauchi, Y. Terauchi, T. Kadowaki, Y. Takeuchi, S. Fukumoto, T. Ikeda, K. Hoshi, U.I. Chung, K. Nakamura, H. Kawaguchi, Regulation of bone formation by adiponectin through autocrine/paracrine and endocrine pathways. J. Cell. Biochem. 99(1), 196–208 (2006)
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Prof. X. H. Luo (the Second XiangYa Hospital of Central South University, Changsha, Hunan, 410011, China) for reading of the manuscript and numerous valuable comments, Prof. Z. G. Wang and Dr. C. G. Deng (Shanghai Research Center for Model Organs) for kindly providing the Adipo−/− mice.
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Qing-ping Wang and Xian-ping Li are contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Qp., Li, Xp., Wang, M. et al. Adiponectin exerts its negative effect on bone metabolism via OPG/RANKL pathway: an in vivo study. Endocrine 47, 845–853 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-014-0216-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-014-0216-z