Abstract
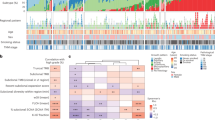
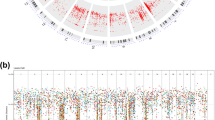
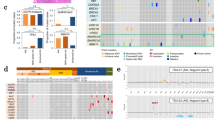
To address the biological heterogeneity of lung cancer, we studied 199 lung adenocarcinomas by integrating genome-wide data on copy number alterations and gene expression with full annotation for major known somatic mutations in this cancer. This showed non-random patterns of copy number alterations significantly linked to EGFR and KRAS mutation status and to distinct clinical outcomes, and led to the discovery of a striking association of EGFR mutations with underexpression of DUSP4, a gene within a broad region of frequent single-copy loss on 8p. DUSP4 is involved in negative feedback control of EGFR signaling, and we provide functional validation for its role as a growth suppressor in EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma. DUSP4 loss also associates with p16/CDKN2A deletion and defines a distinct clinical subset of lung cancer patients. Another novel observation is that of a reciprocal relationship between EGFR and LKB1 mutations. These results highlight the power of integrated genomics to identify candidate driver genes within recurrent broad regions of copy number alteration and to delineate distinct oncogenetic pathways in genetically complex common epithelial cancers.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams J, Cuthbert-Heavens D, Bass S, Knowles MA . (2005). Infrequent mutation of TRAIL receptor 2 (TRAIL-R2/DR5) in transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder with 8p21 loss of heterozygosity. Cancer Lett 220: 137–144.
Adler AS, Lin M, Horlings H, Nuyten DS, van de Vijver MJ, Chang HY . (2006). Genetic regulators of large-scale transcriptional signatures in cancer. Nat Genet 38: 421–430.
Amit I, Citri A, Shay T, Lu Y, Katz M, Zhang F et al. (2007). A module of negative feedback regulators defines growth factor signaling. Nat Genet 39: 503–512.
Armes JE, Hammet F, de SM, Ciciulla J, Ramus SJ, Soo WK et al. (2004). Candidate tumor-suppressor genes on chromosome arm 8p in early-onset and high-grade breast cancers. Oncogene 23: 5697–5702.
Davies H, Hunter C, Smith R, Stephens P, Greenman C, Bignell G et al. (2005). Somatic mutations of the protein kinase gene family in human lung cancer. Cancer Res 65: 7591–7595.
Ding L, Getz G, Wheeler DA, Mardis ER, McLellan MD, Cibulskis K et al. (2008). Somatic mutations affect key pathways in lung adenocarcinoma. Nature 455: 1069–1075.
Ebert BL, Pretz J, Bosco J, Chang CY, Tamayo P, Galili N et al. (2008). Identification of RPS14 as a 5q- syndrome gene by RNA interference screen. Nature 451: 335–339.
Furukawa T, Sunamura M, Motoi F, Matsuno S, Horii A . (2003). Potential tumor suppressive pathway involving DUSP6/MKP-3 in pancreatic cancer. Am J Pathol 162: 1807–1815.
Garnis C, Lockwood WW, Vucic E, Ge Y, Girard L, Minna JD et al. (2006). High resolution analysis of non-small cell lung cancer cell lines by whole genome tiling path array CGH. Int J Cancer 118: 1556–1564.
Ji H, Ramsey MR, Hayes DN, Fan C, McNamara K, Kozlowski P et al. (2007). LKB1 modulates lung cancer differentiation and metastasis. Nature 448: 807–810.
Kendall J, Liu Q, Bakleh A, Krasnitz A, Nguyen KC, Lakshmi B et al. (2007). Oncogenic cooperation and coamplification of developmental transcription factor genes in lung cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104: 16663–16668.
Kobayashi S, Shimamura T, Monti S, Steidl U, Hetherington CJ, Lowell AM et al. (2006). Transcriptional profiling identifies cyclin D1 as a critical downstream effector of mutant epidermal growth factor receptor signaling. Cancer Res 66: 11389–11398.
Kwei KA, Kim YH, Girard L, Kao J, Pacyna-Gengelbach M, Salari K et al. (2008). Genomic profiling identifies TITF1 as a lineage-specific oncogene amplified in lung cancer. Oncogene 27: 3635–3640.
Lee SH, Shin MS, Kim HS, Lee HK, Park WS, Kim SY et al. (1999). Alterations of the DR5/TRAIL receptor 2 gene in non-small cell lung cancers. Cancer Res 59: 5683–5686.
Lowe SW, Sherri CJ . (2003). Tumor suppression by Ink4a-Arf: progress and puzzles. Curr Opin Genet Dev 13: 77–83.
Marks JL, McLellan MD, Zakowski MF, Lash AE, Kasai Y, Broderick S et al. (2007). Mutational analysis of EGFR and related signaling pathway genes in lung adenocarcinomas identifies a novel somatic kinase domain mutation in FGFR4. PLoS ONE 2: e426–e426.
Matsumoto S, Iwakawa R, Takahashi K, Kohno T, Nakanishi Y, Matsuno Y et al. (2007). Prevalence and specificity of LKB1 genetic alterations in lung cancers. Oncogene 26: 5911–5918.
Meyerson M, Franklin WA, Kelley MJ . (2004). Molecular classification and molecular genetics of human lung cancers. Semin Oncol 31: 4–19.
Michaloglou C, Vredeveld LC, Soengas MS, Denoyelle C, Kuilman T, van der Horst CM et al. (2005). BRAFE600-associated senescence-like cell cycle arrest of human naevi. Nature 436: 720–724.
Mounawar M, Mukeria A, Le CF, Hung RJ, Renard H, Cortot A et al. (2007). Patterns of EGFR, HER2, TP53, and KRAS mutations of p14arf expression in non-small cell lung cancers in relation to smoking history. Cancer Res 67: 5667–5672.
O'Reilly KE, Rojo F, She QB, Solit D, Mills GB, Smith D et al. (2006). mTOR inhibition induces upstream receptor tyrosine kinase signaling and activates Akt. Cancer Res 66: 1500–1508.
Ohgaki H, Kleihues P . (2007). Genetic pathways to primary and secondary glioblastoma. Am J Pathol 170: 1445–1453.
Owens DM, Keyse SM . (2007). Differential regulation of MAP kinase signalling by dual-specificity protein phosphatases. Oncogene 26: 3203–3213.
Parsons DW, Jones S, Zhang X, Lin JC, Leary RJ, Angenendt P et al. (2008). An integrated genomic analysis of human glioblastoma multiforme. Science 321: 1807–1812.
Riely GJ, Kris MG, Rosenbaum D, Marks J, Li AR, Chitale DA et al. (2008). Frequency and distinctive spectrum of KRAS mutations in never smokers with lung adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 14: 5731–5734.
Samuels Y, Wang Z, Bardelli A, Silliman N, Ptak J, Szabo S et al. (2004). High frequency of mutations of the PIK3CA gene in human cancers. Science 304: 554.
Sato M, Vaughan MB, Girard L, Peyton M, Lee W, Shames DS et al. (2006). Multiple oncogenic changes (K-RAS(V12), p53 knockdown, mutant EGFRs, p16 bypass, telomerase) are not sufficient to confer a full malignant phenotype on human bronchial epithelial cells. Cancer Res 66: 2116–2128.
Schulze A, Nicke B, Warne PH, Tomlinson S, Downward J . (2004). The transcriptional response to Raf activation is almost completely dependent on mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase activity and shows a major autocrine component. Mol Biol Cell 15: 3450–3463.
Sharma SV, Bell DW, Settleman J, Haber DA . (2007). Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 7: 169–181.
Shaw AT, Meissner A, Dowdle JA, Crowley D, Magendantz M, Ouyang C et al. (2007). Sprouty-2 regulates oncogenic K-ras in lung development and tumorigenesis. Genes Dev 21: 694–707.
Shen WH, Wang J, Wu J, Zhurkin VB, Yin Y . (2006). Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase 2: a novel transcription target of p53 in apoptosis. Cancer Res 66: 6033–6039.
Sweet-Cordero A, Mukherjee S, Subramanian A, You H, Roix JJ, Ladd-Acosta C et al. (2005). An oncogenic KRAS2 expression signature identified by cross-species gene-expression analysis. Nat Genet 37: 48–55.
Takano T, Ohe Y, Sakamoto H, Tsuta K, Matsuno Y, Tateishi U et al. (2005). Epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutations and increased copy numbers predict gefitinib sensitivity in patients with recurrent non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 23: 6829–6837.
Tanaka H, Yanagisawa K, Shinjo K, Taguchi A, Maeno K, Tomida S et al. (2007). Lineage-specific dependency of lung adenocarcinomas on the lung development regulator TTF-1. Cancer Res 67: 6007–6011.
The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network (2008). Comprehensive genomic characterization defines human glioblastoma genes and core pathways. Nature 455: 1061–1068.
Tresini M, Lorenzini A, Torres C, Cristofalo VJ . (2007). Modulation of replicative senescence of diploid human cells by nuclear ERK signaling. J Biol Chem 282: 4136–4151.
Weir BA, Woo MS, Getz G, Perner S, Ding L, Beroukhim R et al. (2007). Characterizing the cancer genome in lung adenocarcinoma. Nature 450: 893–898.
Zhu CQ, Blackhall FH, Pintilie M, Iyengar P, Liu N, Ho J et al. (2004). Skp2 gene copy number aberrations are common in non-small cell lung carcinoma, and its overexpression in tumors with ras mutation is a poor prognostic marker. Clin Cancer Res 10: 1984–1991.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Agnes Viale and the MSKCC Genomics Core Laboratory personnel for the generation of microarray data; Dr Laetitia Borsu for assistance with Sequenom assays; Drs Hakim Djaballah and Gabriela E. Sanchez of the MSKCC HTS Core Facility for providing GFP siRNAs; Louis Vargas, Yonghong Xiao and the MSKCC Pathology Core personnel for technical assistance; Drs William Travis, Andre Moreira and David Klimstra for providing pathologic diagnoses; Drs John Minna and Adi Gazdar for providing the human bronchial epithelial cell (HBEC) lines; Drs Alice H Berger, Marasu Niki and Pier Paolo Pandolfi for assistance with reagents and related studies; Dr Roman Thomas for sharing unpublished microarray data, and Dr Harold Varmus for support (to RS). Barry S Taylor is a graduate student in the Department of Physiology and Biophysics, Weill Cornell Graduate School of Medical Sciences. We acknowledge the support of the National Cancer Institute (U01-CA84999 to WG, P01-CA129243 to ML), the Doris Duke Charitable Foundation (to WP), the Long Island League to Abolish Cancer (to WP), the Labrecque Foundation (to WG) and the Lung Cancer Research Foundation (to ML). The MSKCC Sequenom facility is supported by the Anbinder Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chitale, D., Gong, Y., Taylor, B. et al. An integrated genomic analysis of lung cancer reveals loss of DUSP4 in EGFR-mutant tumors. Oncogene 28, 2773–2783 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.135
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.135
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Graph-based multi-modality integration for prediction of cancer subtype and severity
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Signature-driven repurposing of Midostaurin for combination with MEK1/2 and KRASG12C inhibitors in lung cancer
Nature Communications (2023)
-
High expression levels of pyrimidine metabolic rate–limiting enzymes are adverse prognostic factors in lung adenocarcinoma: a study based on The Cancer Genome Atlas and Gene Expression Omnibus datasets
Purinergic Signalling (2020)
-
A co-expressed gene status of adenylate kinase 1/4 reveals prognostic gene signature associated with prognosis and sensitivity to EGFR targeted therapy in lung adenocarcinoma
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
REG4 is an indicator for KRAS mutant lung adenocarcinoma with TTF-1 low expression
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2019)